What is a Low Voltage Motor and How Does it Work in Different Applications
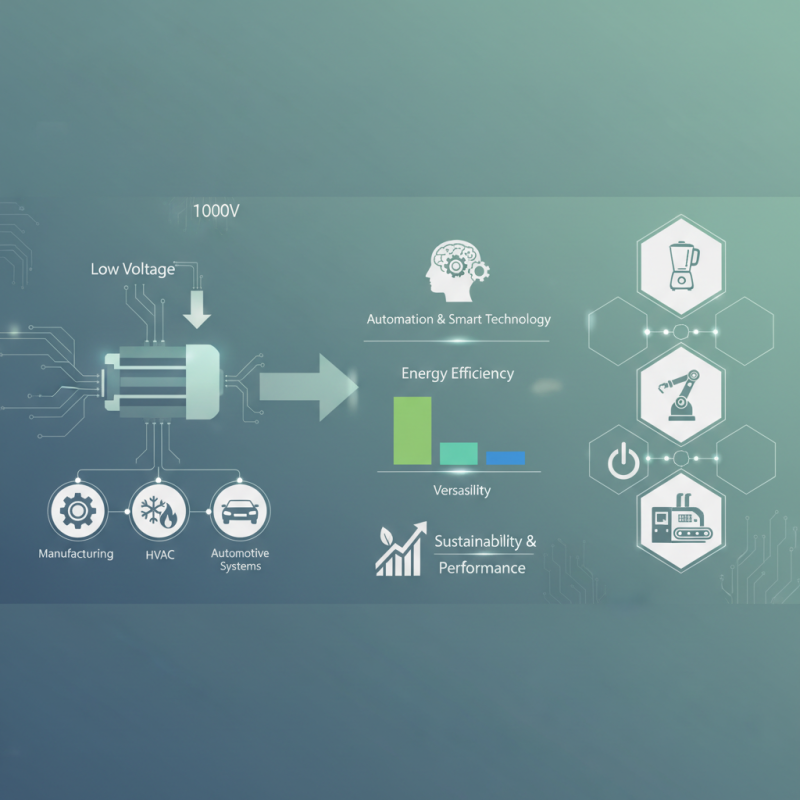
In the realm of electromechanical systems, the role of low voltage motors is increasingly paramount. These motors, typically operating at voltages below 1000V, have found extensive applications across various industries including manufacturing, HVAC, and automotive systems. As noted by industry expert Dr. Emily Johnson, "Low Voltage Motors are the backbone of modern automation, allowing for efficient and reliable operation across a myriad of applications." Her insights highlight the critical nature of these motors in ensuring the seamless functionality of machinery and equipment.
Low voltage motors are characterized by their ability to provide substantial power while maintaining energy efficiency and versatility. Their design allows them to be easily integrated into different systems, making them ideal for everything from small appliances to large-scale industrial machinery. As industries lean towards automation and smart technology, understanding how low voltage motors function, along with their benefits and challenges, becomes essential for engineers and technical professionals alike.
The increased adoption of low voltage motors reflects a broader trend towards energy efficiency and sustainability in technology. By exploring how these motors work in various applications and their impact on efficiency and performance, we can better appreciate their significance within today's evolving landscape of industrial technology.
What Defines a Low Voltage Motor in Electrical Engineering
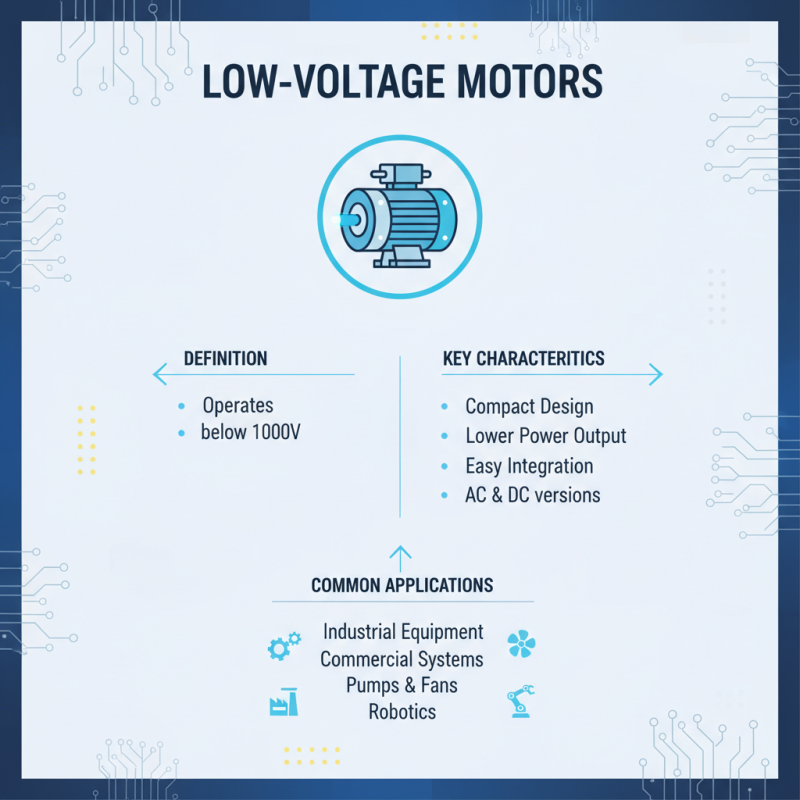
A low voltage motor is defined in electrical engineering as any motor that operates at voltages typically below 1000 volts. These motors are widely utilized in various industrial and commercial applications due to their efficiency, reliability, and ease of control. Characteristics that distinguish low voltage motors include their compact design, lower power output, and the ability to be easily integrated into existing systems. They often come in AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) versions, each suited for different operational requirements.
One of the primary reasons low voltage motors are prevalent is their adaptability to multiple uses. In manufacturing, they drive conveyors, pumps, and fans, providing the necessary motion with precise control. In the HVAC sector, they are essential for air circulation and temperature regulation. Additionally, low voltage motors find applications in household appliances, from washing machines to garden tools, demonstrating their versatility across various fields. Their ability to operate safely at lower voltages makes them suitable for environments where the risk of electric shock must be minimized, further enhancing their appeal in modern engineering solutions.
Key Components of Low Voltage Motors and Their Functions
Low voltage motors are integral to many industrial and commercial applications, and their functionality relies on several key components. One of the primary elements is the rotor, which is the rotating part of the motor that generates mechanical energy. When electric current flows through the stator winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces rotation in the rotor. This transformation of electrical energy into mechanical energy is essential for driving various machines and systems.
Another crucial component is the stator, which houses the winding and is stationary. The stator's design significantly influences the motor's efficiency and performance. It consists of laminated silicon steel core, which minimizes energy losses due to eddy currents. Additionally, low voltage motors typically include bearings that support the rotor and allow it to turn smoothly. These bearings are essential for reducing friction and wear, thus enhancing the motor's lifespan and operational reliability. Together, these components work in harmony to ensure that low voltage motors operate efficiently across diverse applications, from fan drives to conveyor systems, making them vital in modern machinery.
What is a Low Voltage Motor and How Does it Work in Different Applications
| Application Area |
Type of Low Voltage Motor |
Key Components |
Functions |
| Pumps |
Induction Motor |
Stator, Rotor, Bearings |
Convert electrical energy to rotational motion, circulate fluids |
| Conveyor Systems |
Synchronous Motor |
Stator, Rotor, Control System |
Provide constant speed and torque for material handling |
| HVAC Systems |
Blower Motor |
Fan, Armature, Commutator |
Drive fans to circulate air for heating or cooling |
| Industrial Robotics |
Servo Motor |
Encoder, Gearbox, Controller |
Precise control of position, speed, and torque for automation |
| Home Appliances |
Universal Motor |
Commutator, Brushes, Windings |
Power various small appliances efficiently |
Working Principles: How Low Voltage Motors Operate
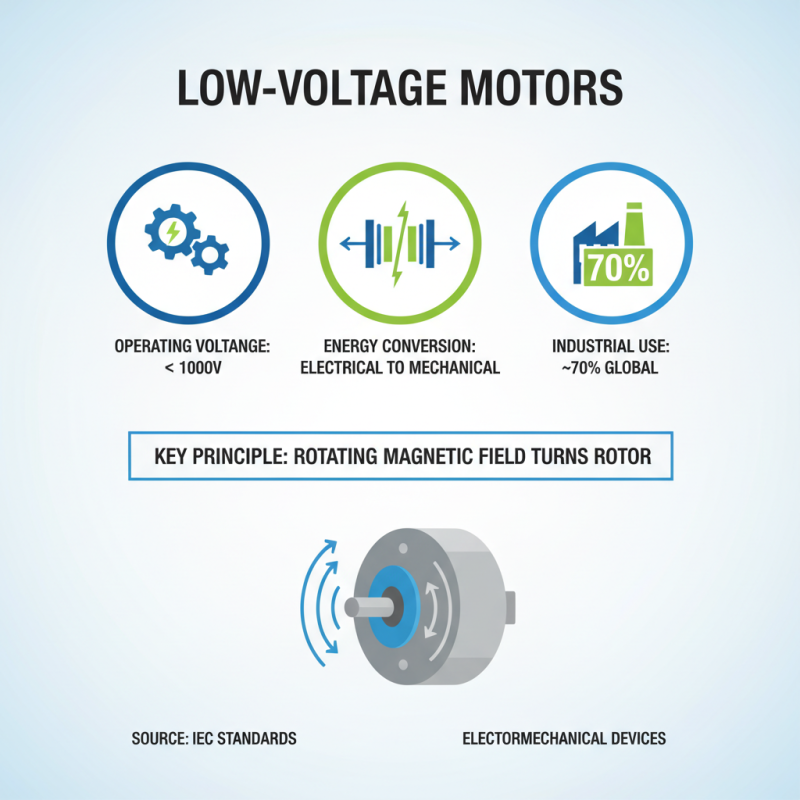
Low voltage motors are electromechanical devices designed to operate efficiently at voltages typically below 1,000 volts. These motors leverage electromagnetic principles to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, primarily through the interaction of magnetic fields generated by currents flowing through coils. The basic working principle involves the creation of a rotating magnetic field in the stator, which induces a current in the rotor, causing it to turn. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), low voltage motors are essential in a multitude of applications, accounting for nearly 70% of all industrial motor usage globally.
In practical applications, low voltage motors are widely utilized across various sectors, including manufacturing, HVAC systems, and renewable energy. For instance, in an industrial setting, these motors are crucial in driving fans, pumps, and conveyors, showcasing their versatility. Reports by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) indicate that the efficiency of low voltage motors has improved significantly over the past decade, with modern designs achieving efficiency ratings of over 95%. This advancement not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with global sustainability efforts by minimizing energy consumption. Furthermore, their compact design and ease of integration make low voltage motors a preferred choice for electric vehicle applications and home automation systems, reflecting their growing importance in today's energy-conscious world.
Common Applications of Low Voltage Motors in Industry
Low voltage motors are extensively utilized across various industries due to their efficiency and reliability in operations. According to a recent industry report, low voltage motors account for nearly 60% of the global motor market, highlighting their critical role in supporting industrial operations. These motors typically operate at voltages below 1000 volts and are designed for moderate power applications, making them suitable for a broad range of tasks.
In industrial settings, low voltage motors are employed in numerous applications, including pumps, fans, and conveyor systems. For instance, in the manufacturing sector, these motors are often used in production lines, where they power conveyor belts that transport materials and products efficiently. The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE) noted that upgrading to high-efficiency low voltage motors could enhance energy savings by as much as 15-20%, significantly reducing operational costs for manufacturers. Similarly, in HVAC systems, low voltage motors are crucial for driving compressors and blowers, ensuring optimal indoor climate control while minimizing energy consumption.
Moreover, the versatility of low voltage motors extends to the food processing industry, where they are vital in mixing, grinding, and packaging applications. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that motors are responsible for approximately 70% of industrial energy consumption, underscoring the importance of efficient motor use. By utilizing low voltage motors, industries can not only achieve enhanced productivity but also align with sustainability goals through reduced energy demands, promoting a greener approach in manufacturing and processing environments.
Advantages of Using Low Voltage Motors for Various Applications
Low voltage motors (LVMs) have gained significant traction in various industrial applications due to their efficient performance and adaptability. One of the most notable advantages of low voltage motors is their ability to operate at lower energy consumption levels compared to their high voltage counterparts. This characteristic is particularly important in an era where energy efficiency is paramount. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), approximately 70% of electrical energy used in industry is consumed by electric motors, emphasizing the need for optimizing motor performance and selecting more efficient models like low voltage motors.
In diverse applications ranging from HVAC systems to conveyor belts in manufacturing, low voltage motors provide remarkable flexibility and reliability. Their design allows for easier integration into existing systems without requiring substantial modifications. Industry data highlights that low voltage motors can support a range of operational speeds and torque requirements, making them ideal for applications in home appliances, electric vehicles, and industrial automation. Furthermore, the lower operational voltage enhances safety and reduces the risk of electrical hazards, providing an added layer of protection for both equipment and personnel.
Additionally, low voltage motors are known for their lower maintenance costs and longer service life. A study by the European Commission reflected that the lifecycle costs of low voltage motors, including maintenance and energy expenses, can be reduced by up to 30% when compared to traditional high voltage motors. This aspect makes them not only an environmentally friendly choice but also a financially sound investment for companies aiming to improve their operational efficiency and minimize downtime.

Home
Products
SIEMENS Gearmotor
 SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor
SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor  SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor
SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor  SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage  SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor
SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor  SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150
SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150  SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS V90
SIEMENS SINAMICS V90  SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage  FLENDER Gear Unit
FLENDER Gear Unit  FLENDER Helical Gear Unit
FLENDER Helical Gear Unit  Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears
Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears  FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox
FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox  Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance
Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance  Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents
Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents  SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox
SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox  Playmaker In The Premium League
Playmaker In The Premium League  Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox
Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox  Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections
Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections  Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces
Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces  Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200
Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200  Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill
Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill  The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox
The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox  Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox
Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox  Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox
Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox  The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships
The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships  Reliable Power Generation on board
Reliable Power Generation on board  Maximum performance level, fast deliverable
Maximum performance level, fast deliverable  Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills
Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills  Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.
Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.  FLENDER Coupling
FLENDER Coupling  ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling  ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling  N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling  N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling
N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling 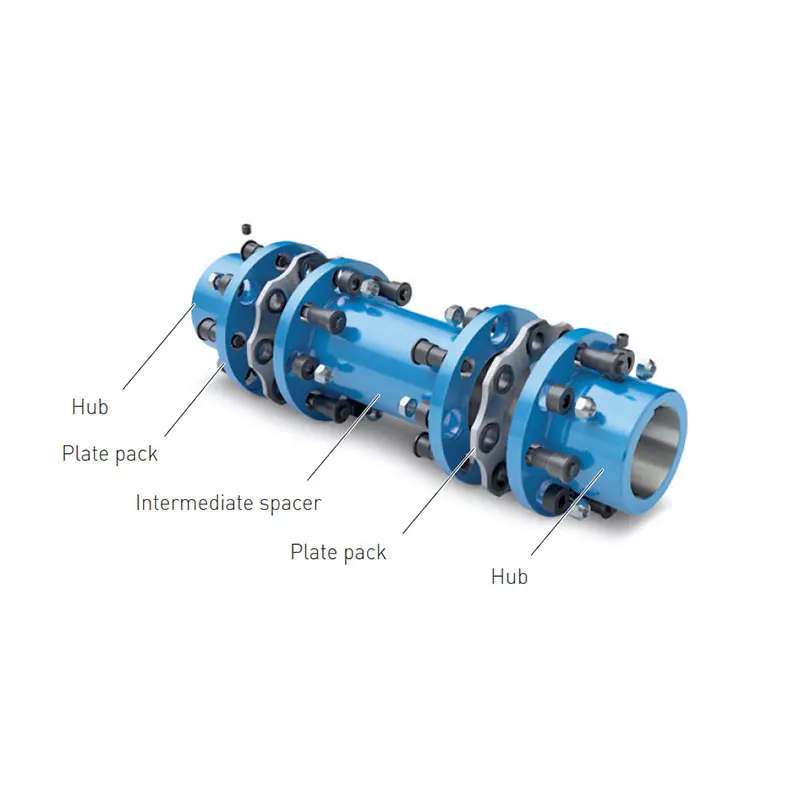 ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts
ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts  N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling
N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling  RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling  N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling
N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling  ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling
ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling  ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance  ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance  FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance
FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance  SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance
SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance  BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance
BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance  FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance
FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance  SEW Gearmotor
SEW Gearmotor
Our Company
News
Case
Contact Us
 R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage
R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage
F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage
K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage
S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor
W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor