-
Home
-
Products
-
SIEMENS Gearmotor
-
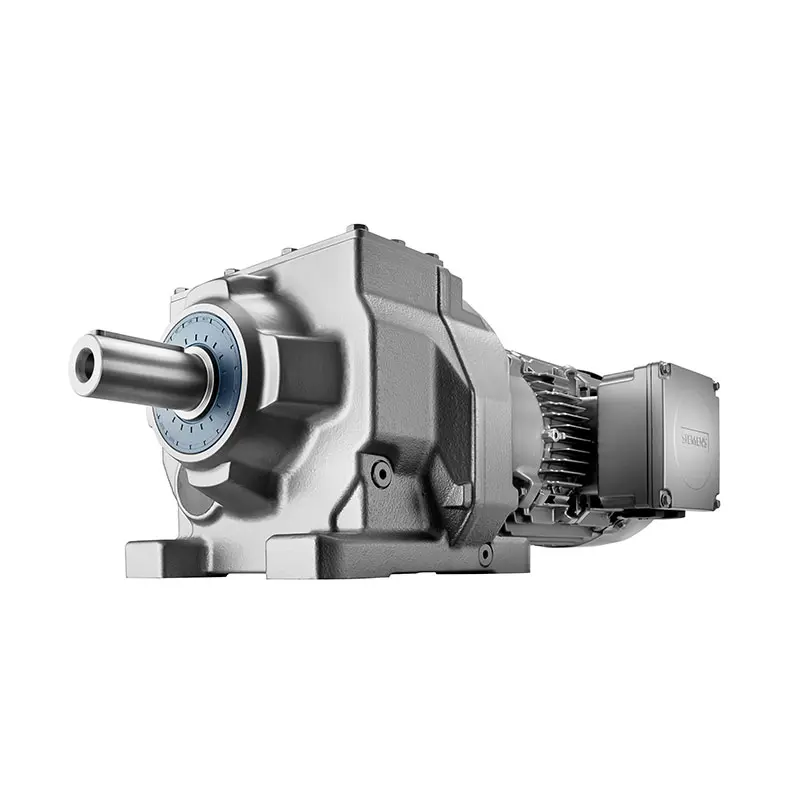 SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage -
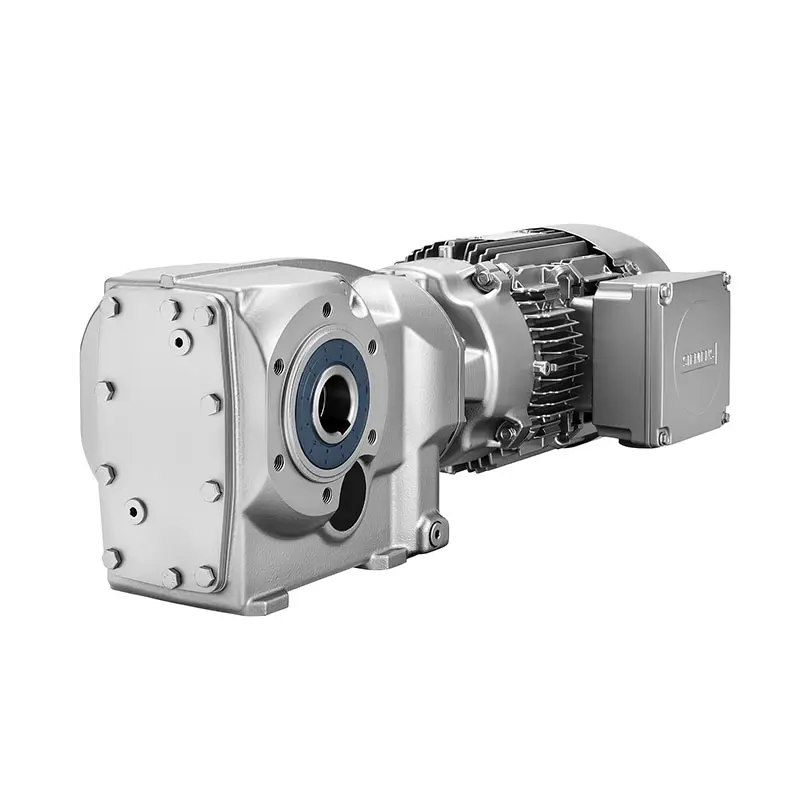 SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor
SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor -
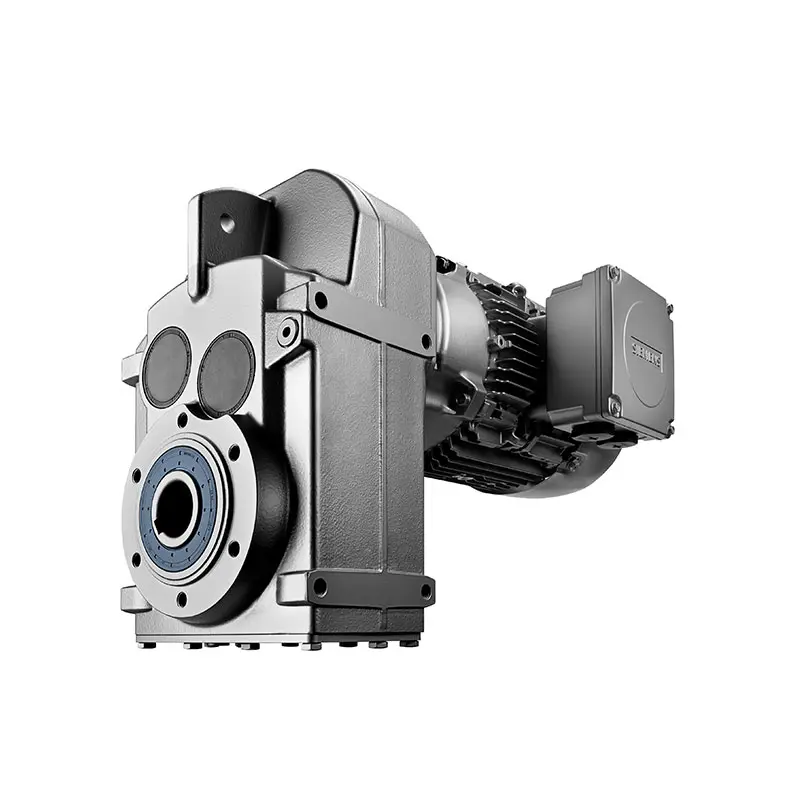 SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor
SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor -
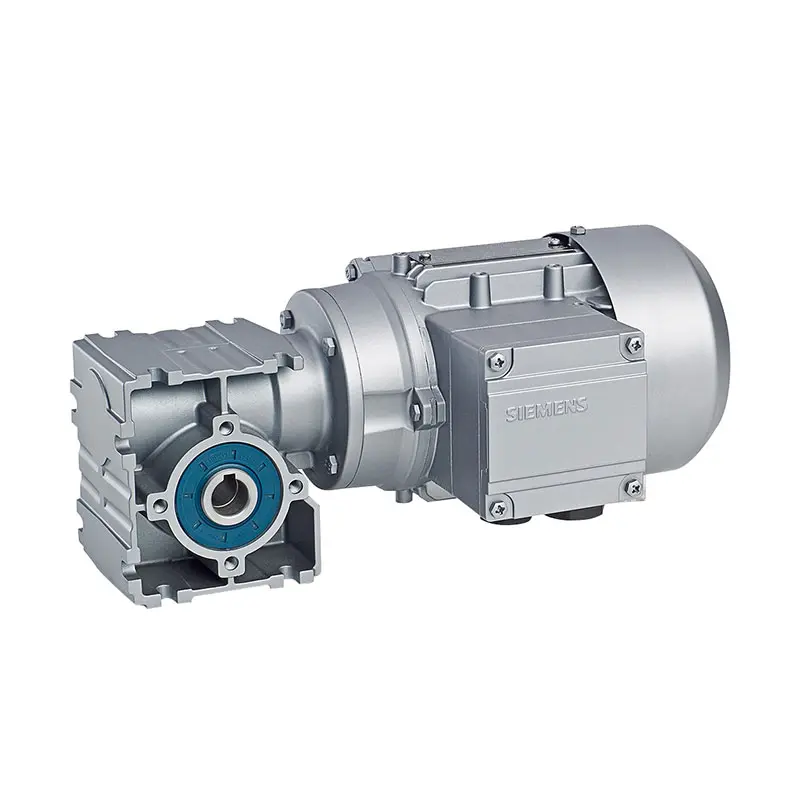 SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage -
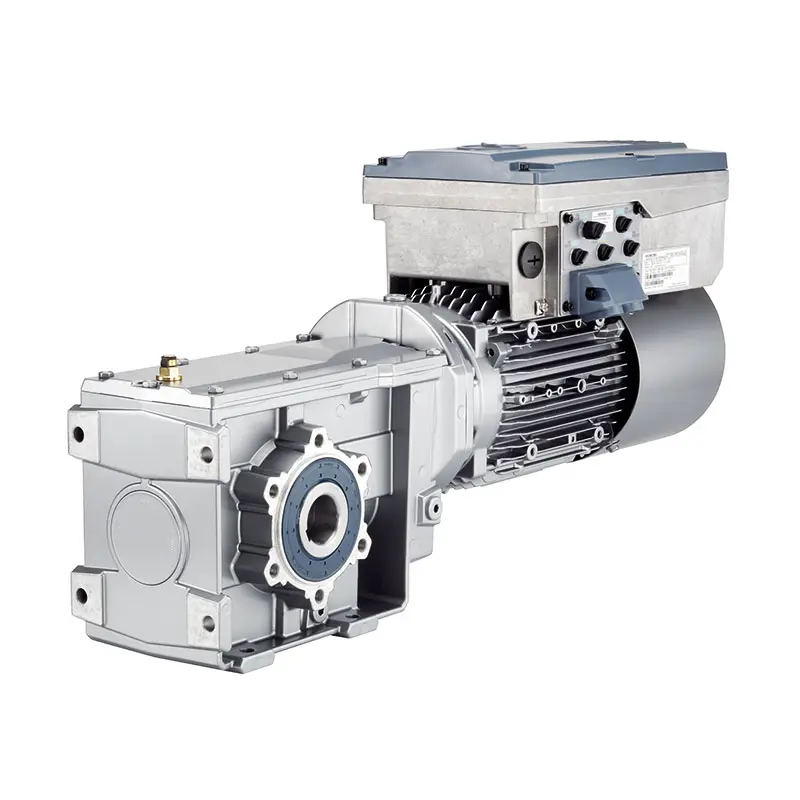 SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor
SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor -
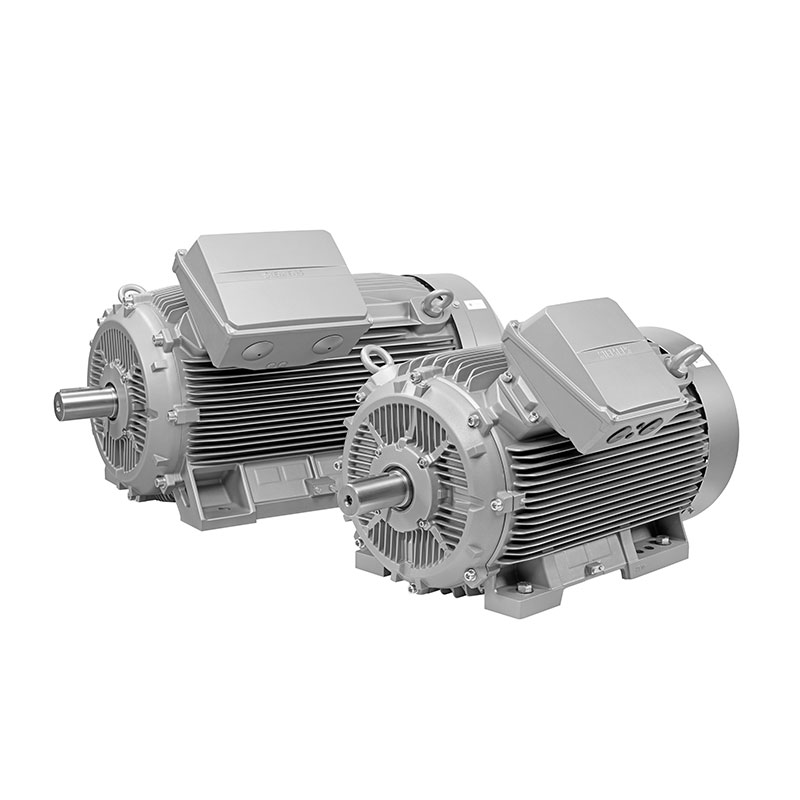 SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage -
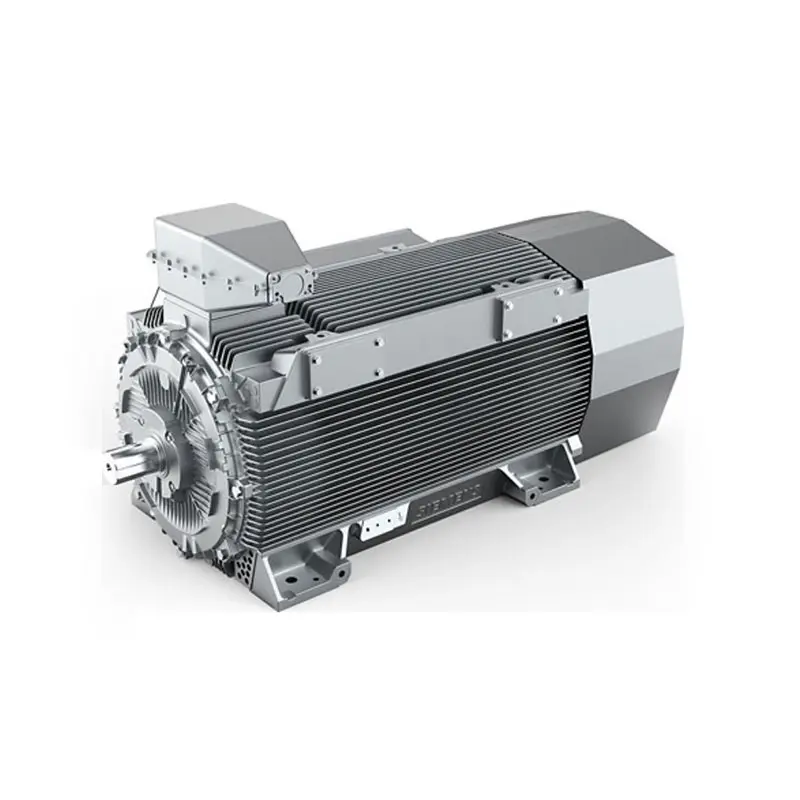 SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage -
 SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage -
 SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage -
 SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage -
 SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage -
 SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage -
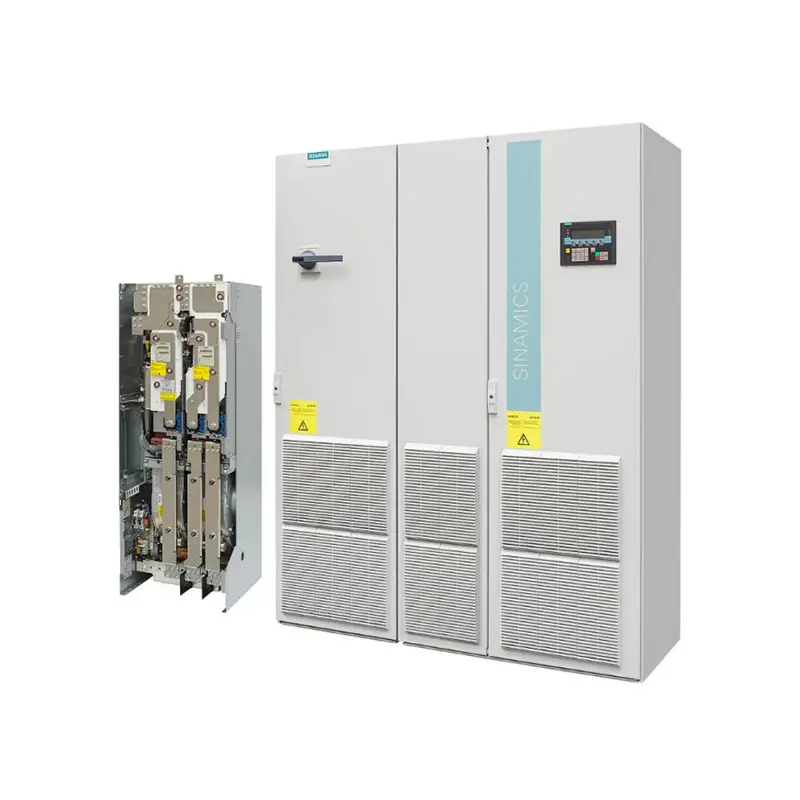 SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150
SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150 -
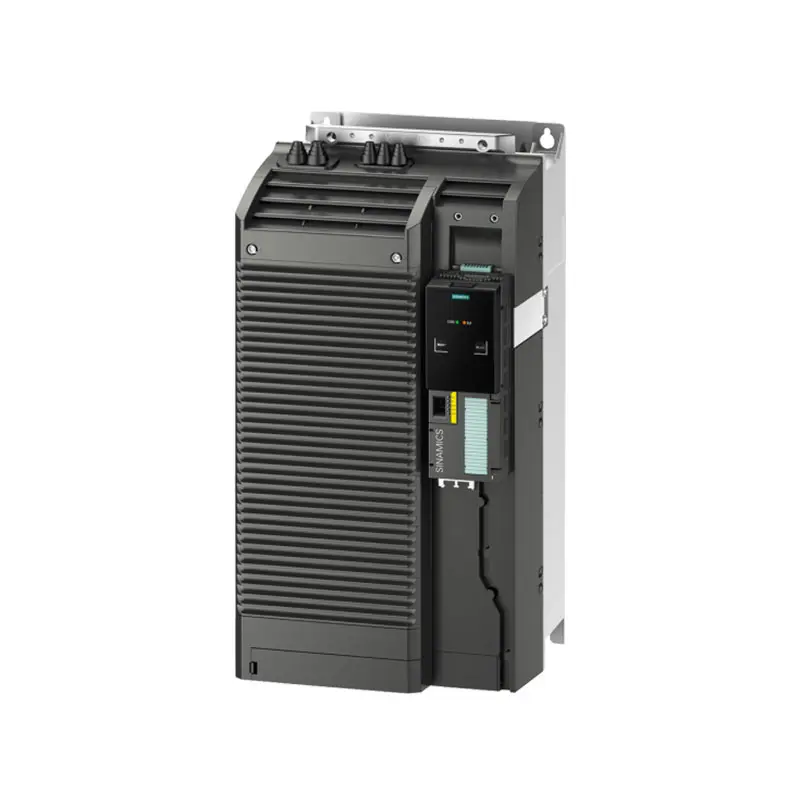 SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage -
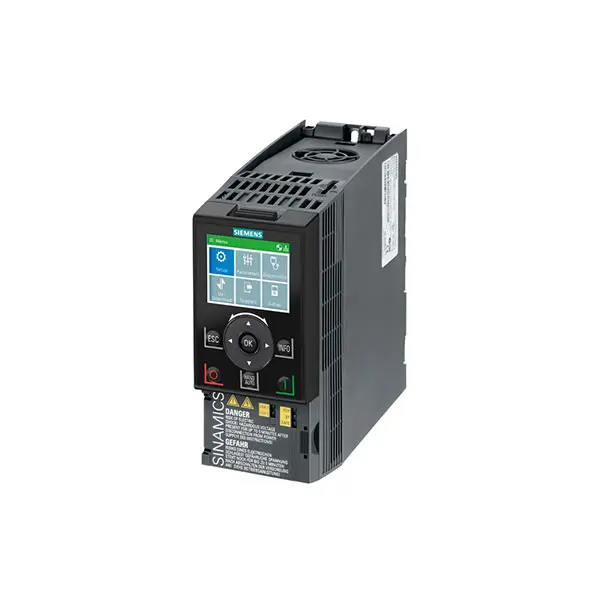 SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage -
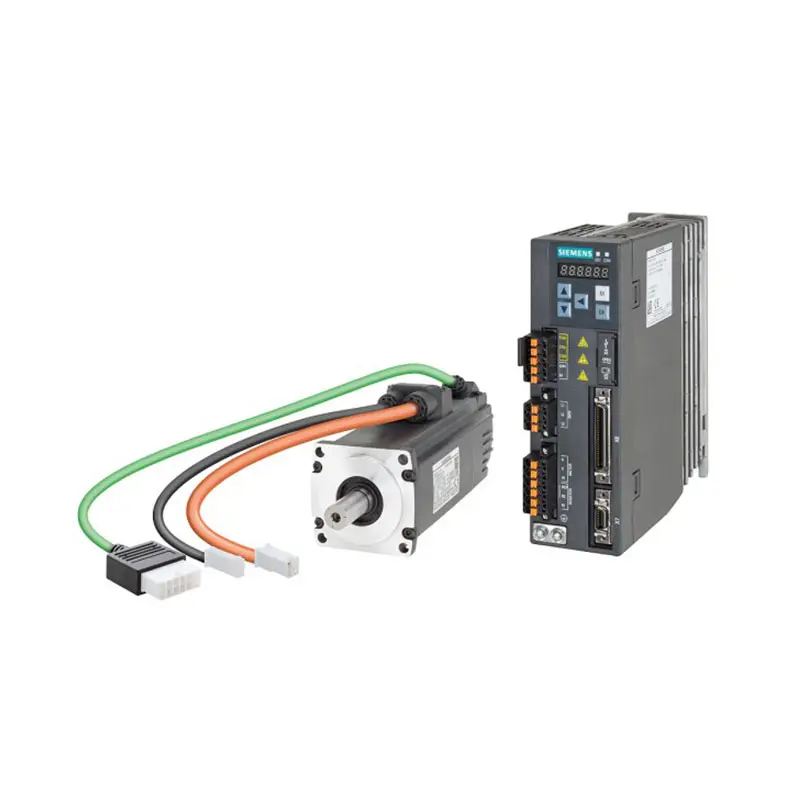 SIEMENS SINAMICS V90
SIEMENS SINAMICS V90 -
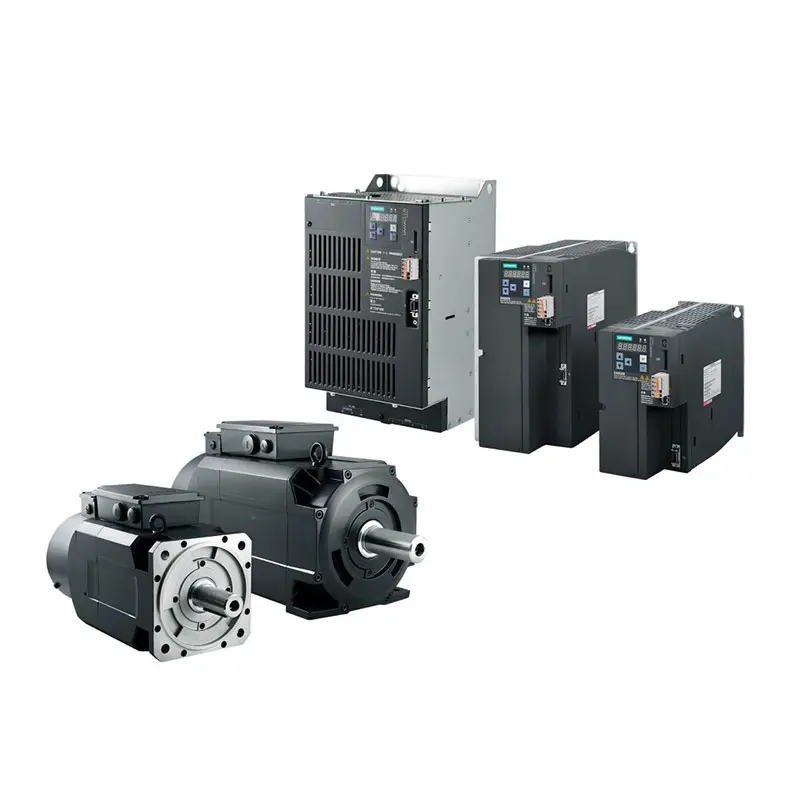 SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage
-
-
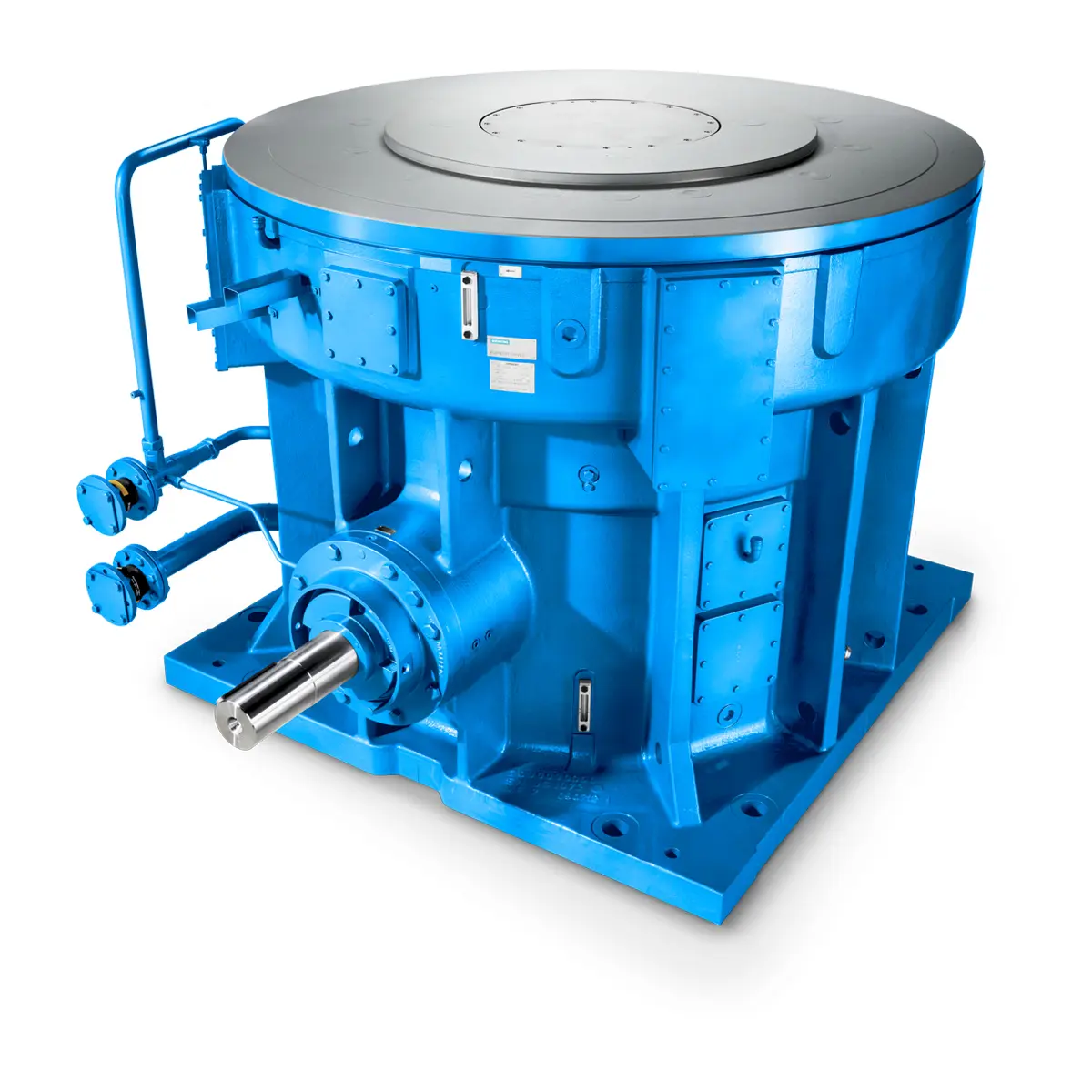
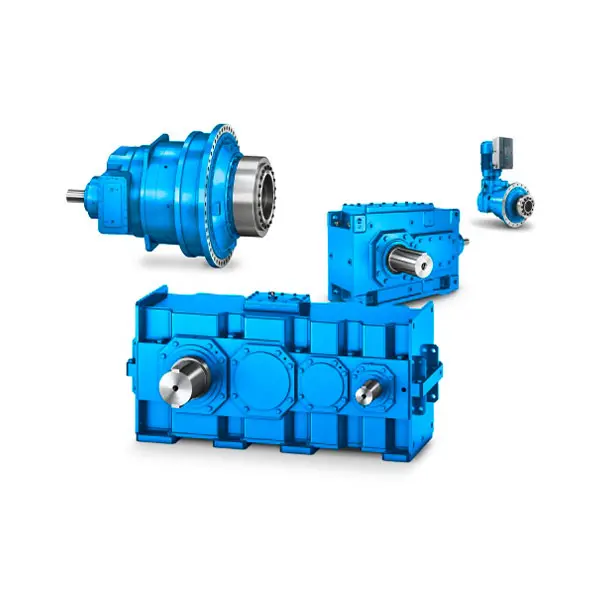 FLENDER Gear Unit
FLENDER Gear Unit -
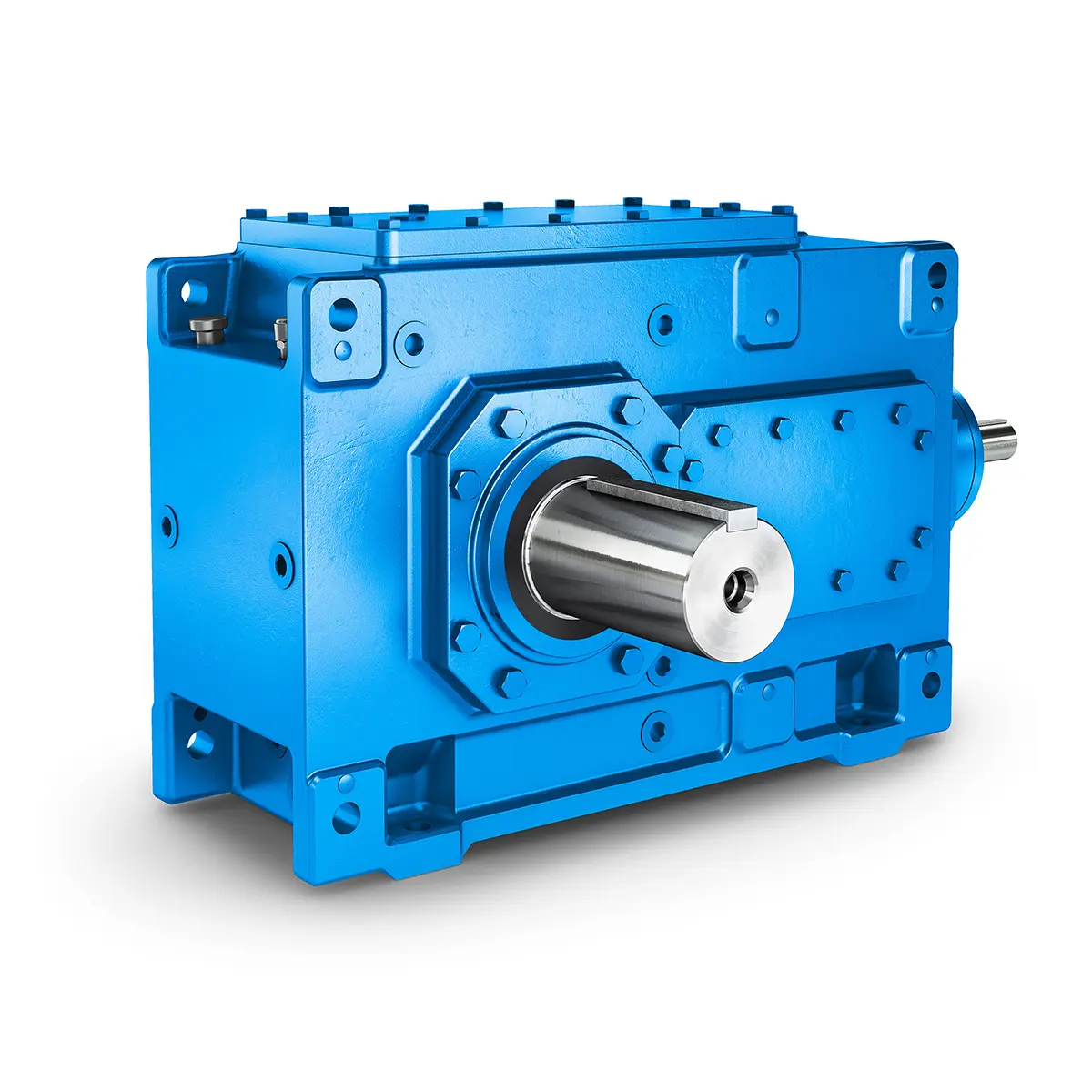 FLENDER Helical Gear Unit
FLENDER Helical Gear Unit -
 Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears
Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears -
 FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox
FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox -
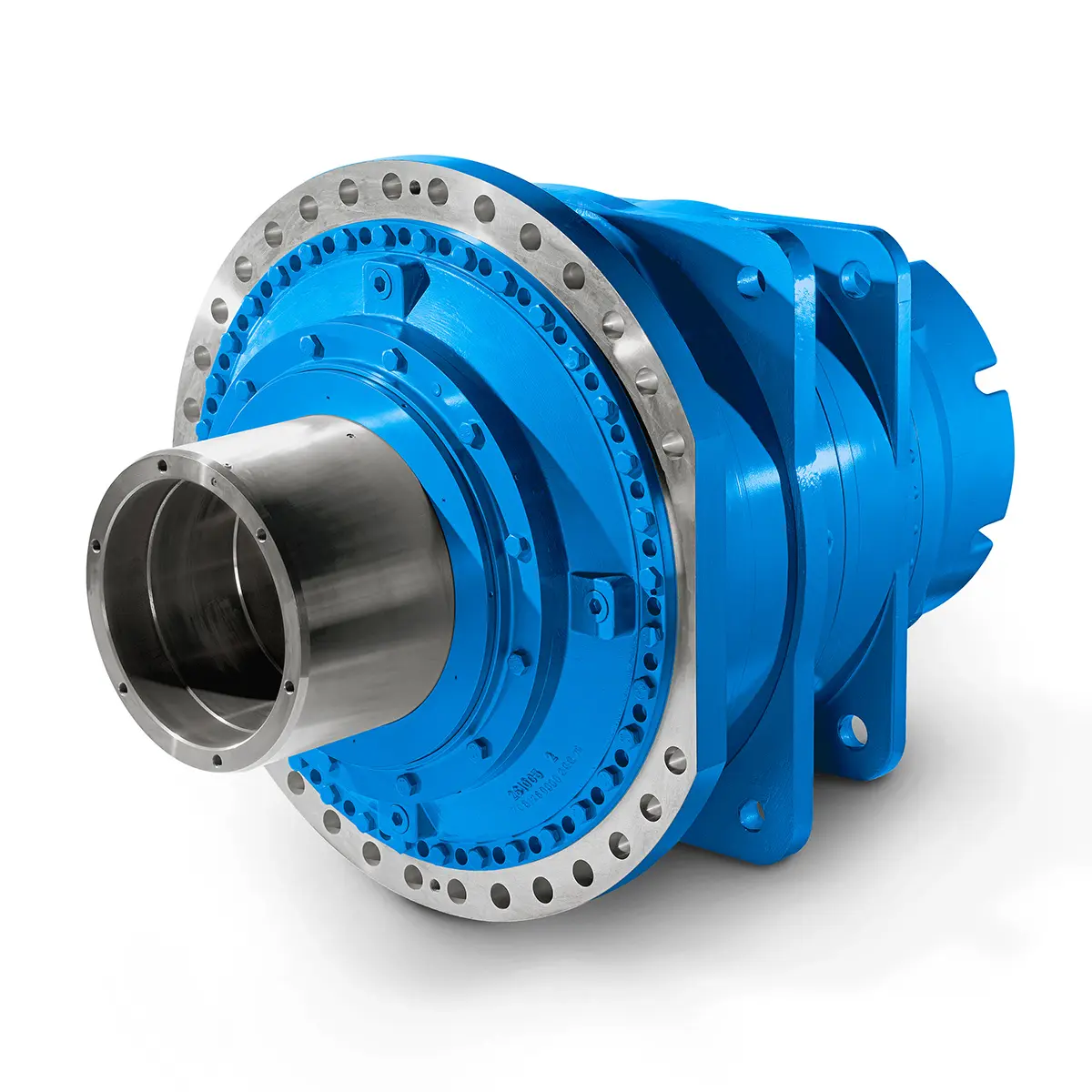 Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance
Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance -
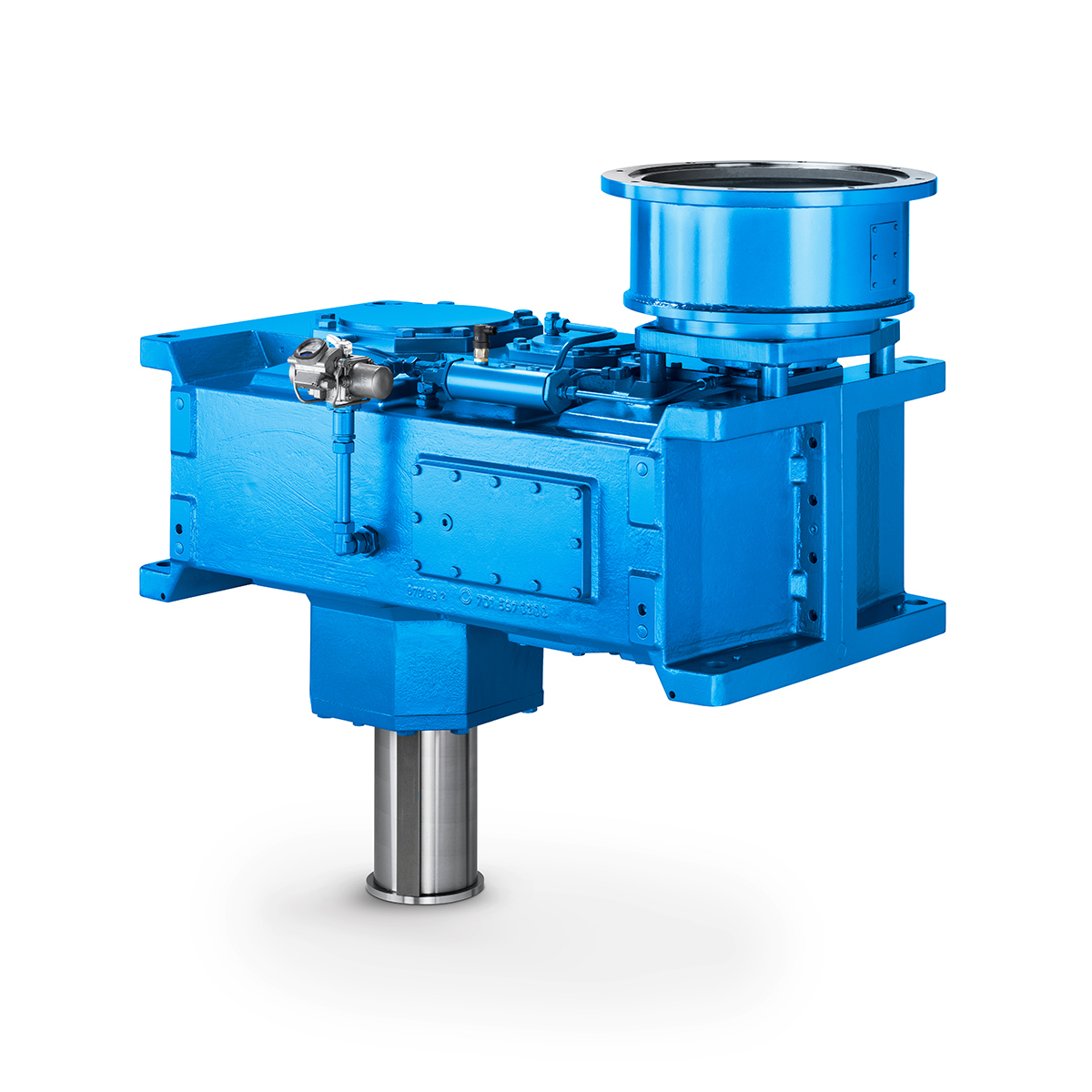 Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents
Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents -
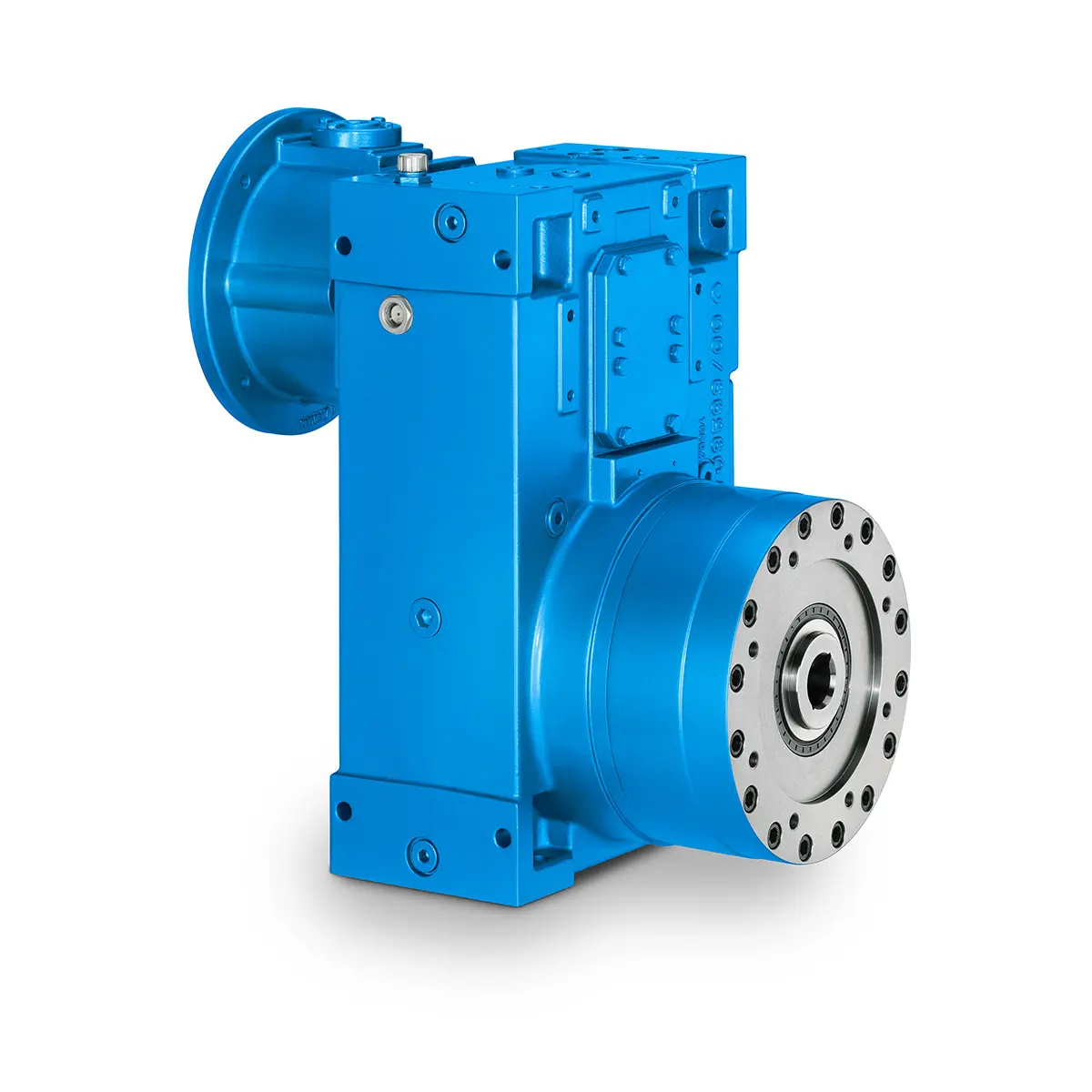 SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox
SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox -
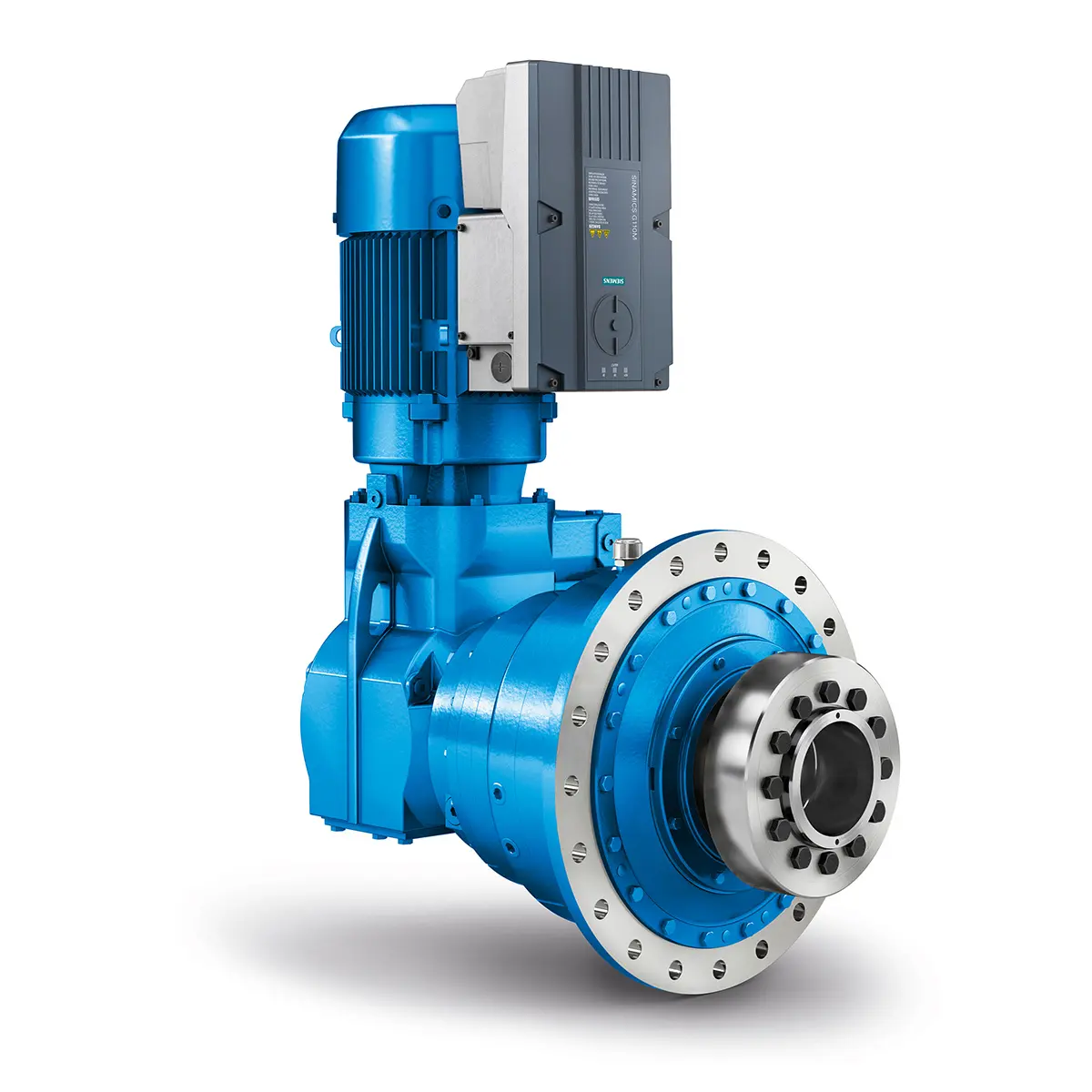 Playmaker In The Premium League
Playmaker In The Premium League -
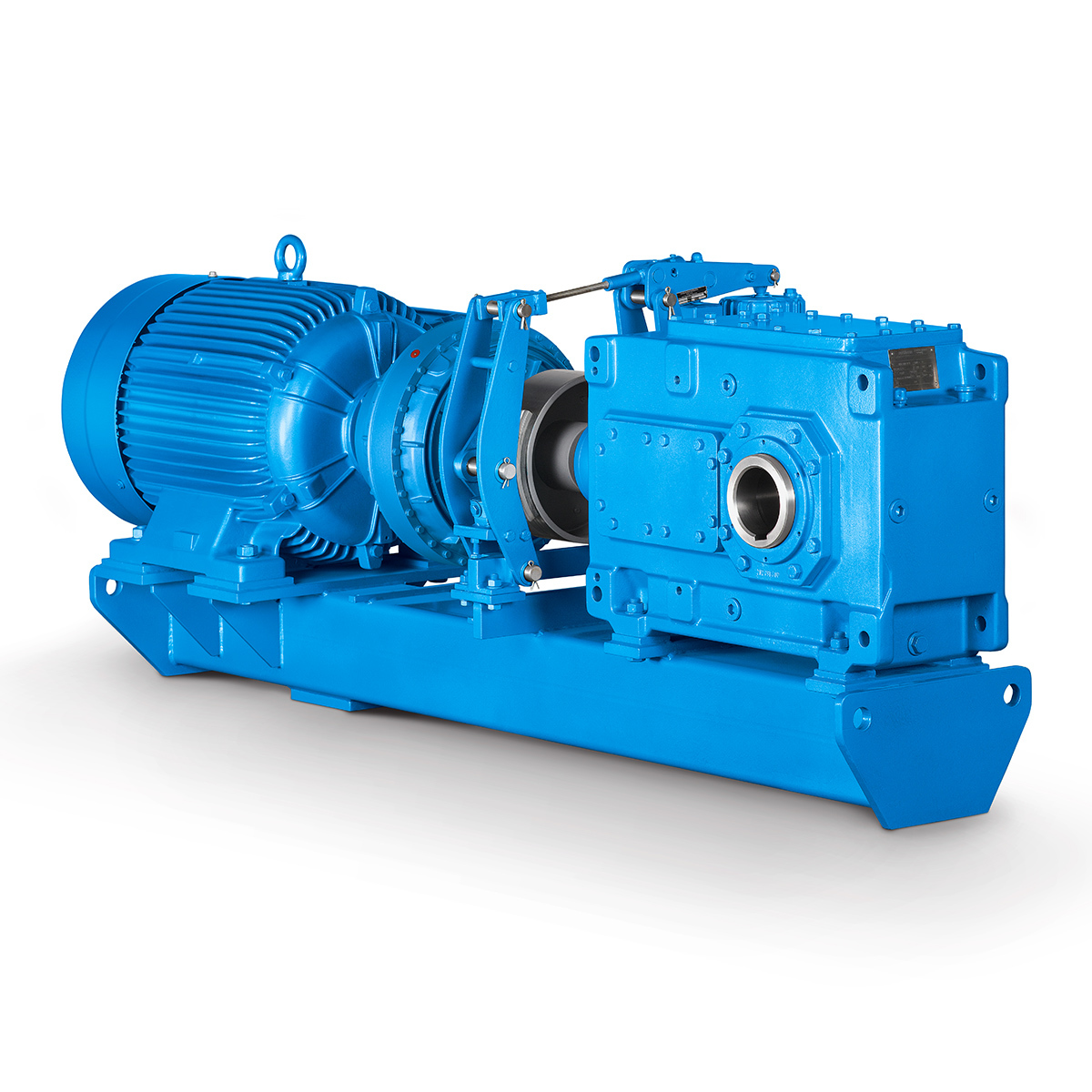 Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox
Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox -
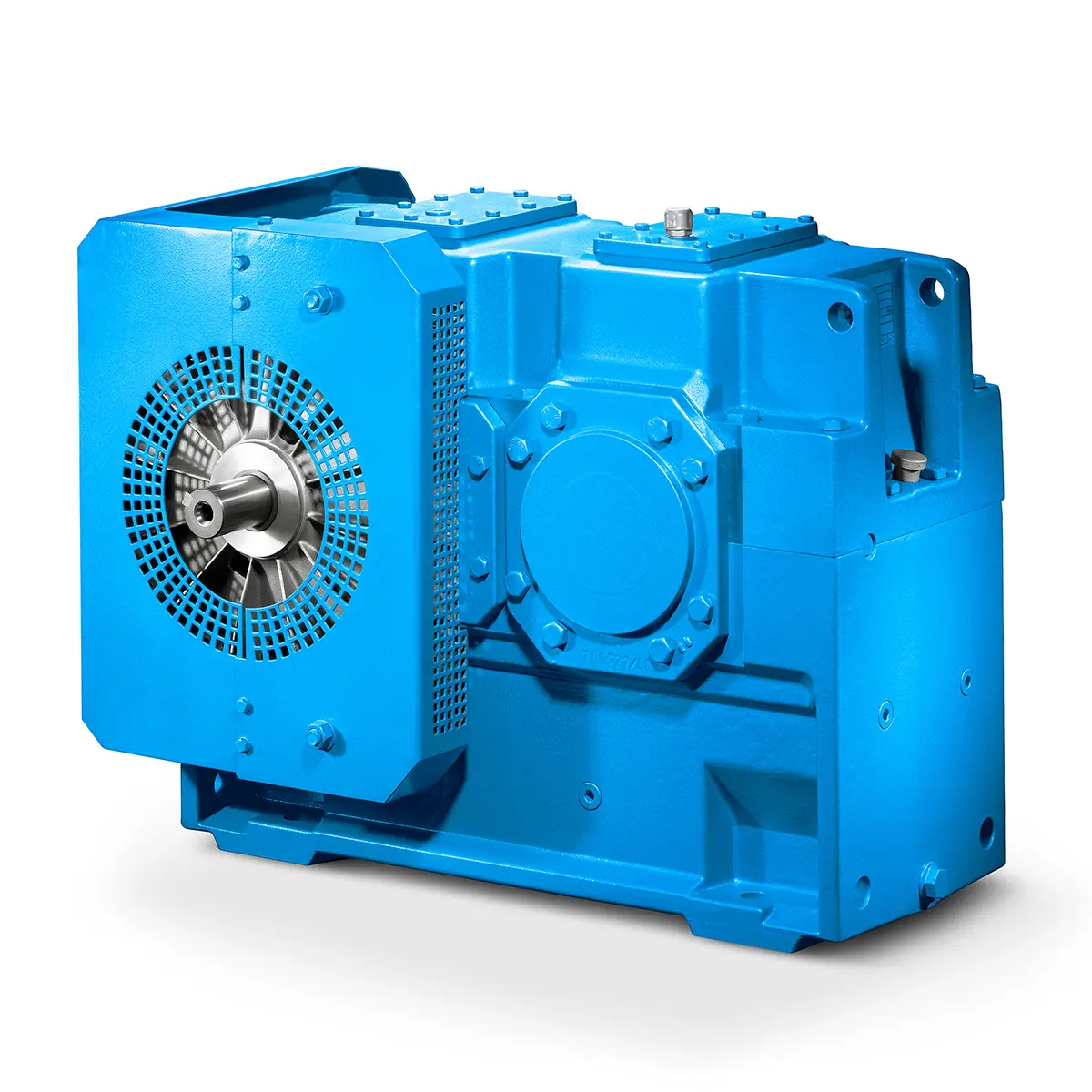 Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections
Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections -
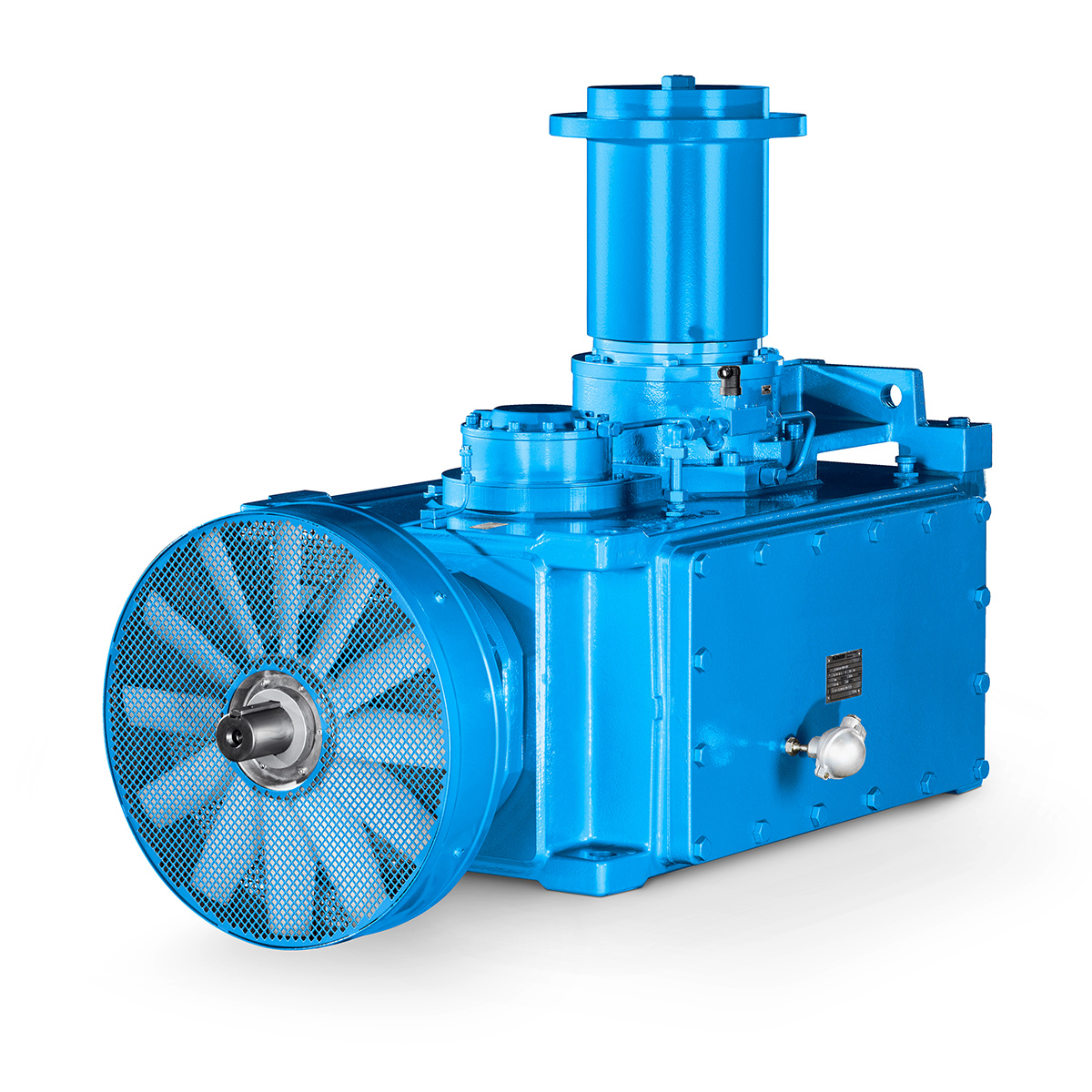 Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces
Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces -
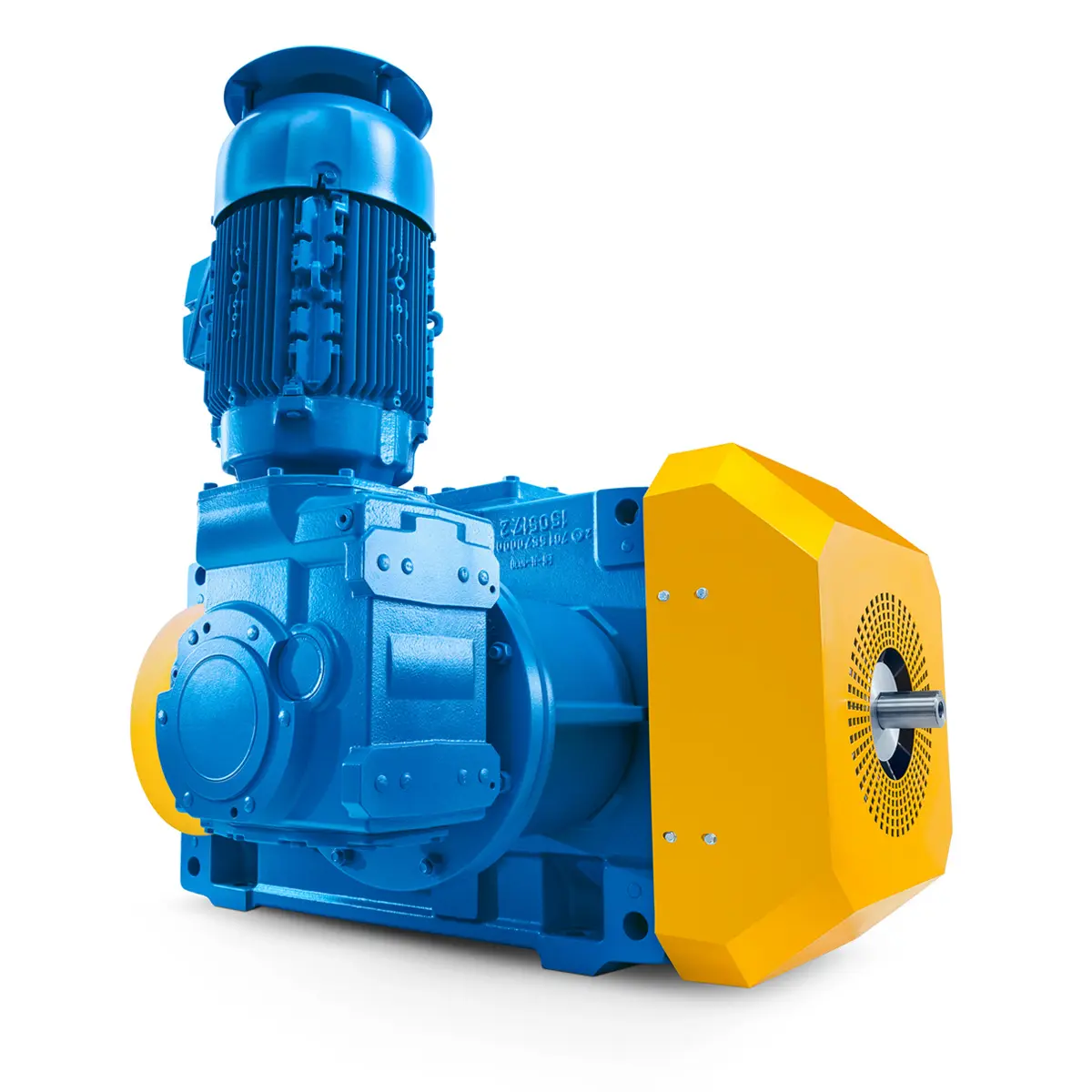 Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200
Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200 -
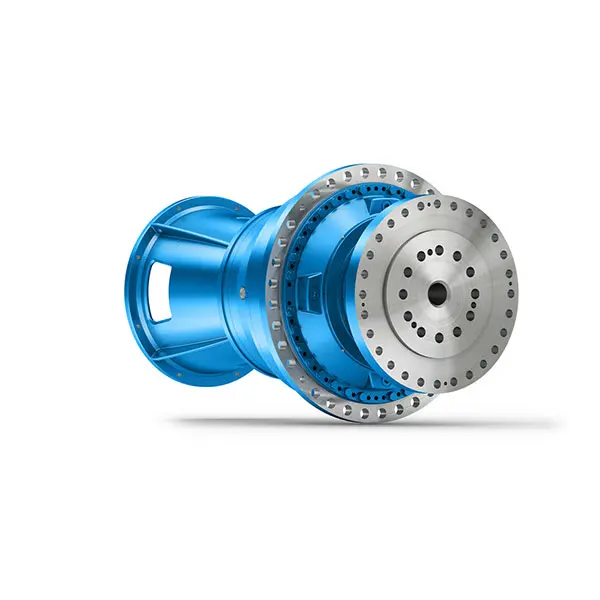 Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill
Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill -
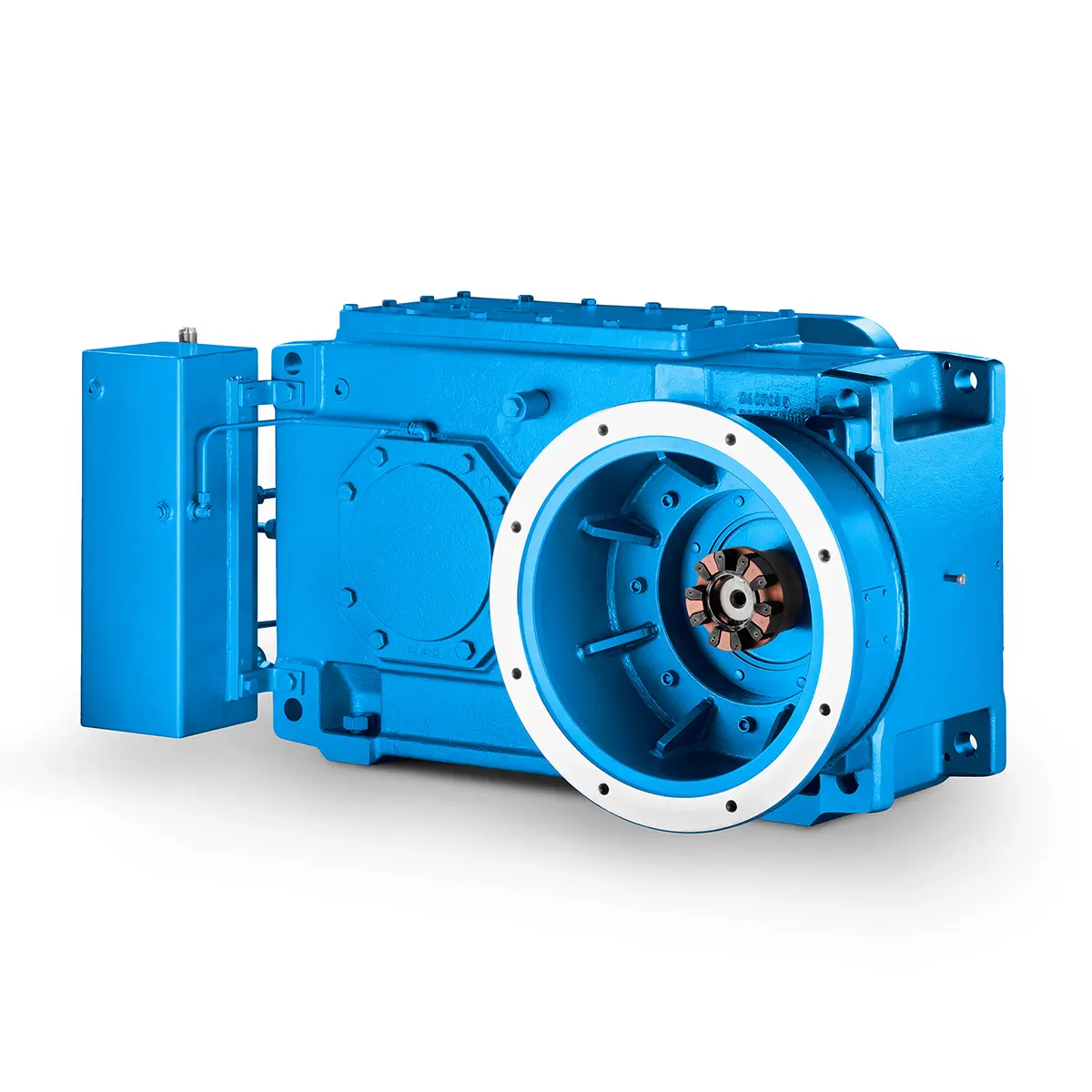
 The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox
The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox -
 Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox
Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox -
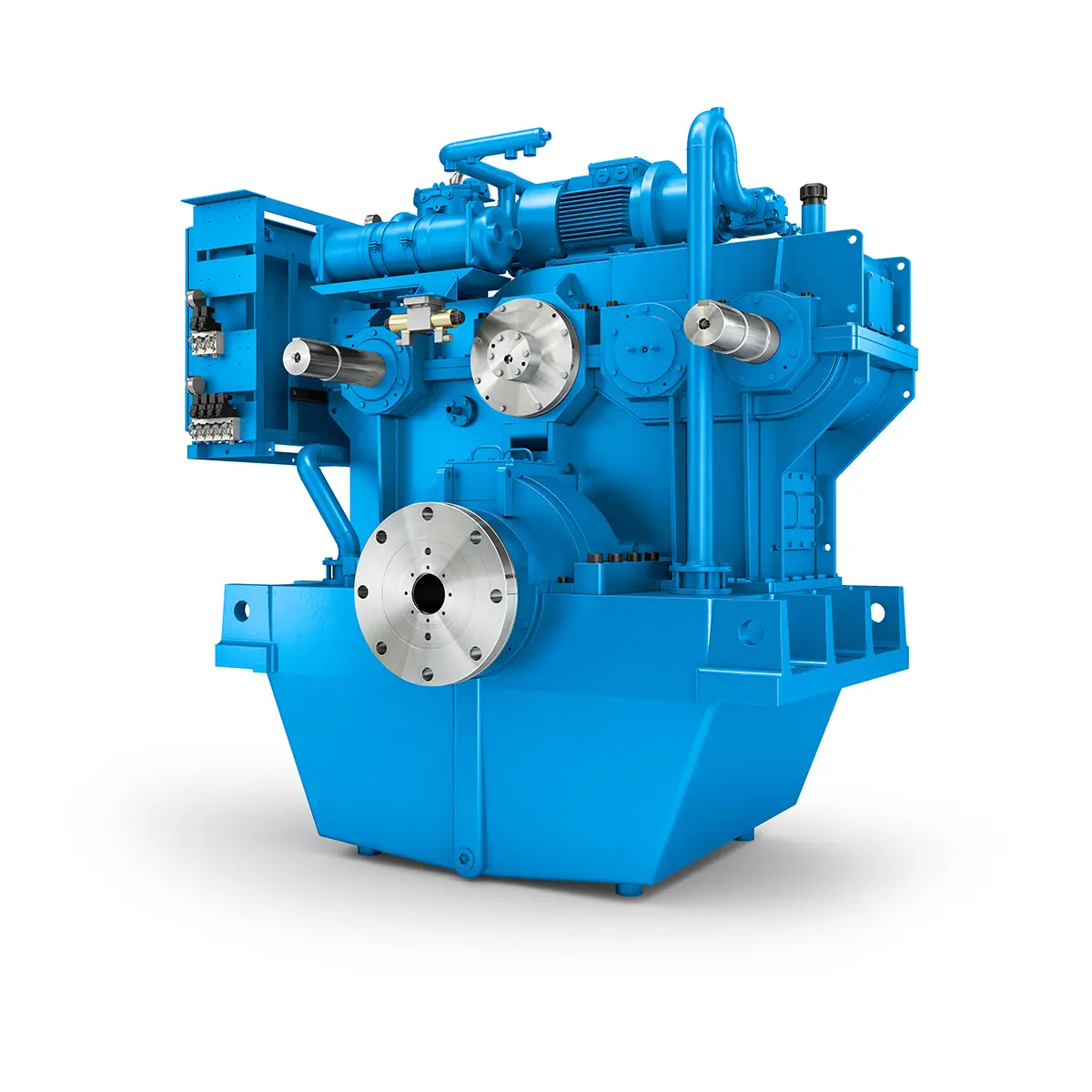 Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox
Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox -
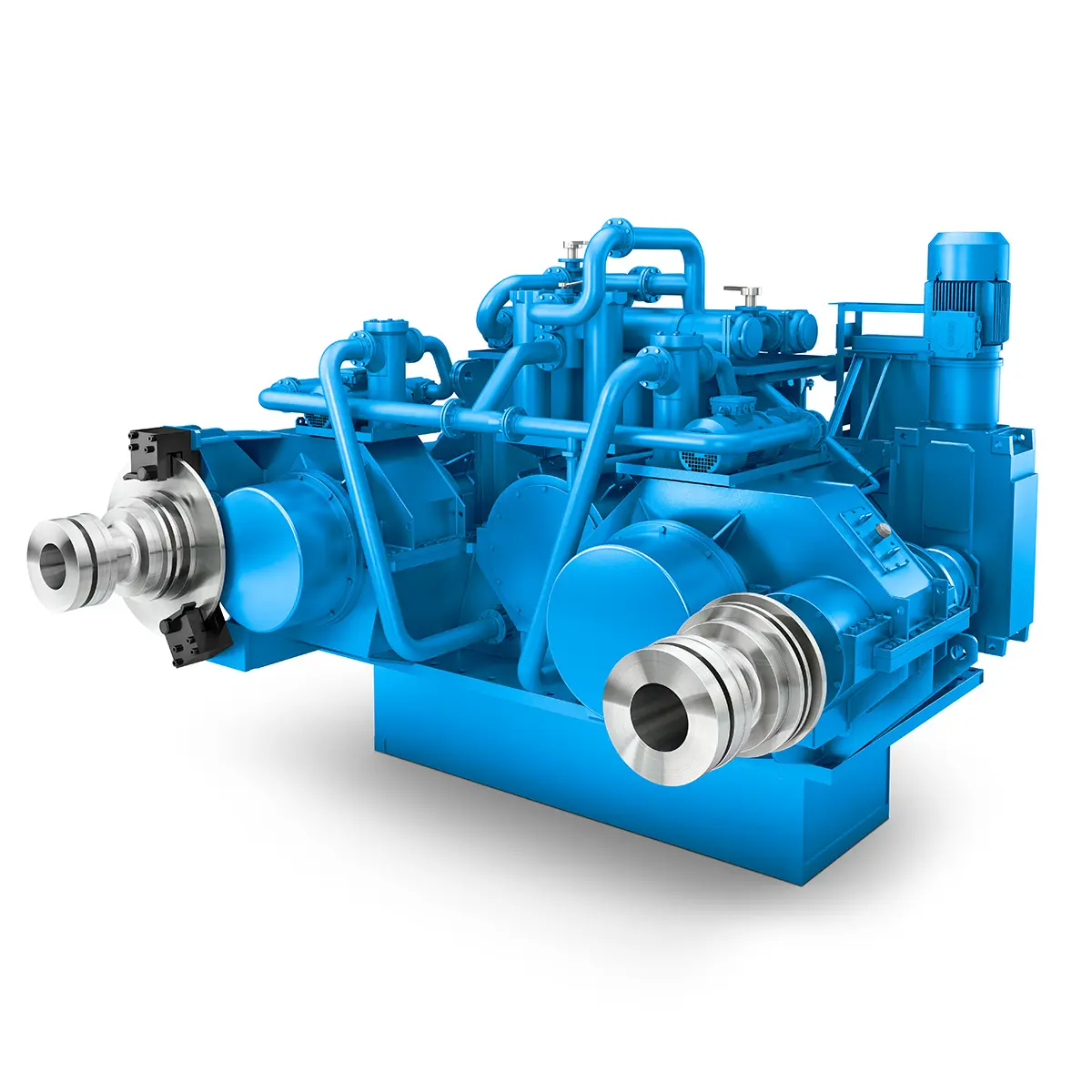 The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships
The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships -
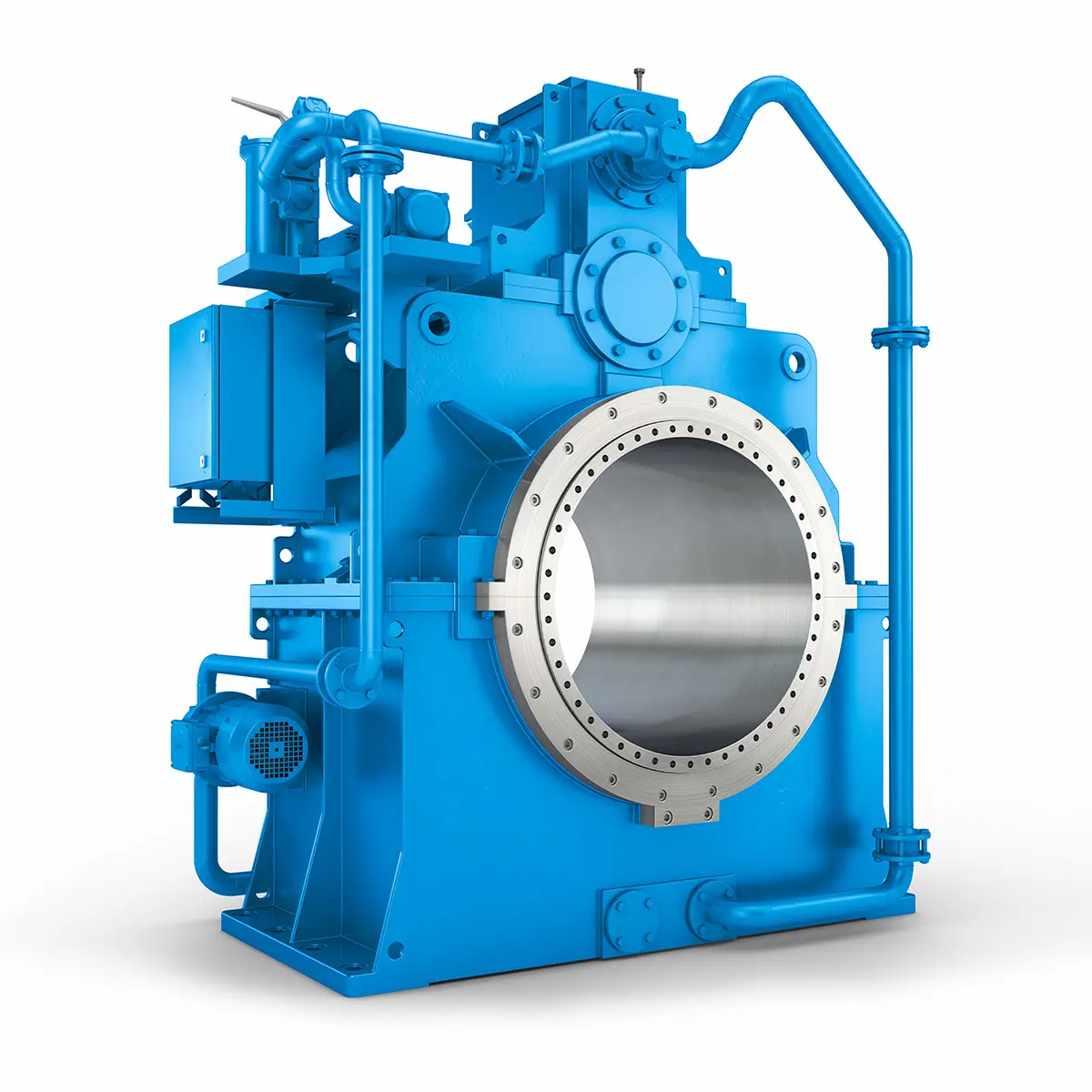 Reliable Power Generation on board
Reliable Power Generation on board -
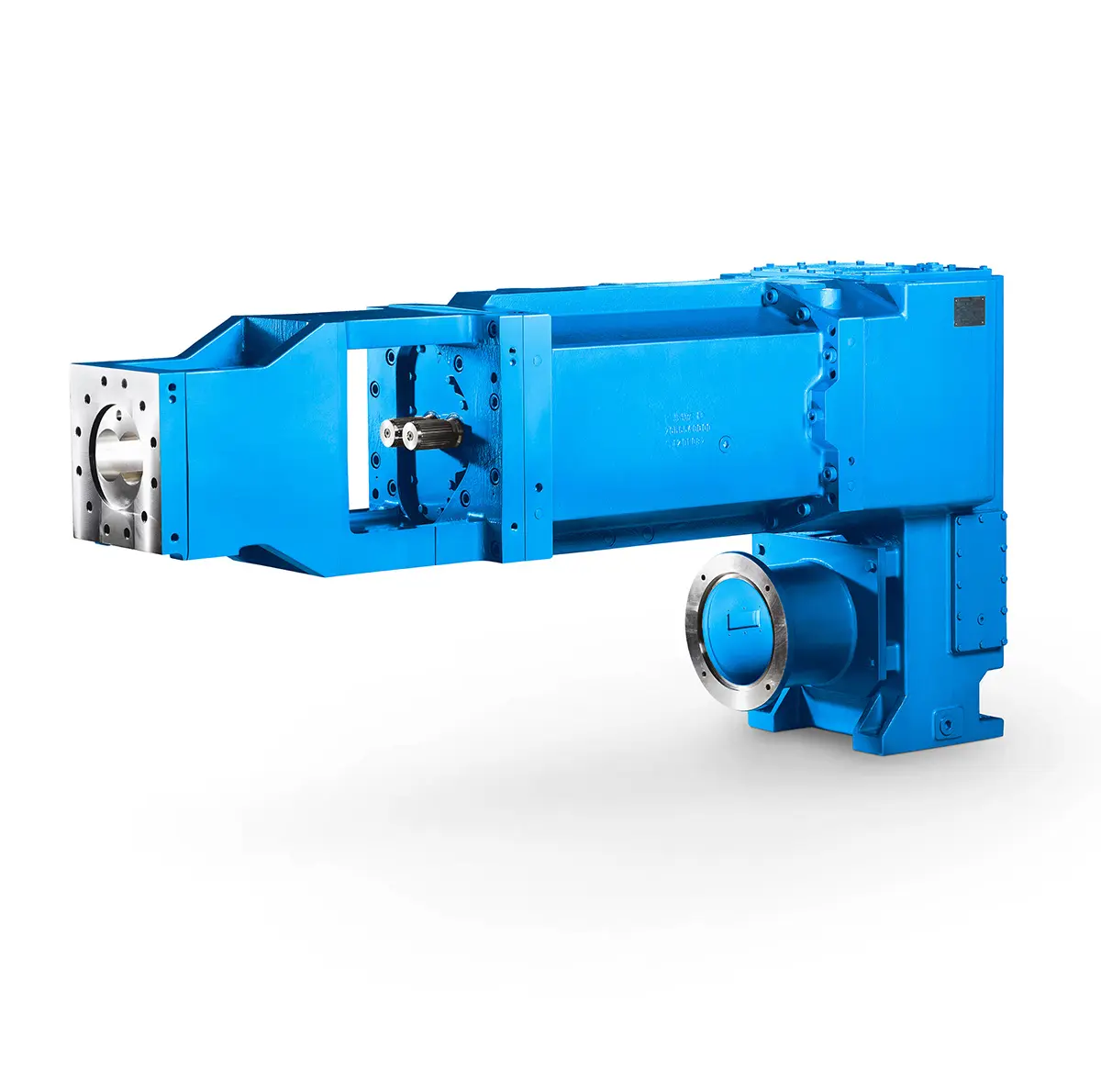 Maximum performance level, fast deliverable
Maximum performance level, fast deliverable -
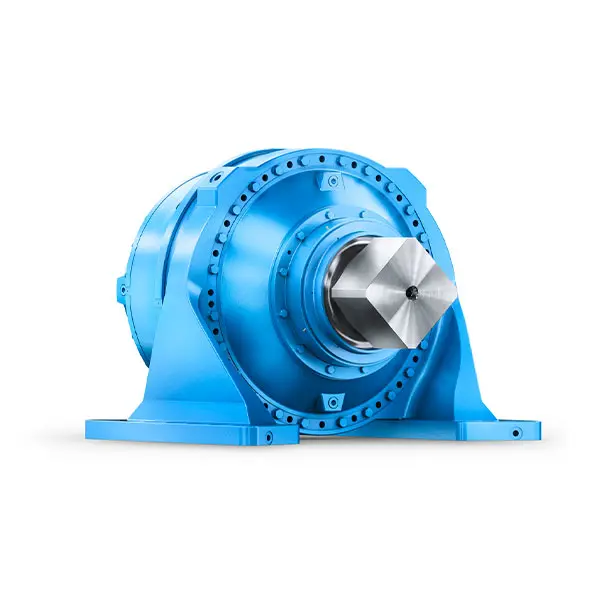 Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills
Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills -
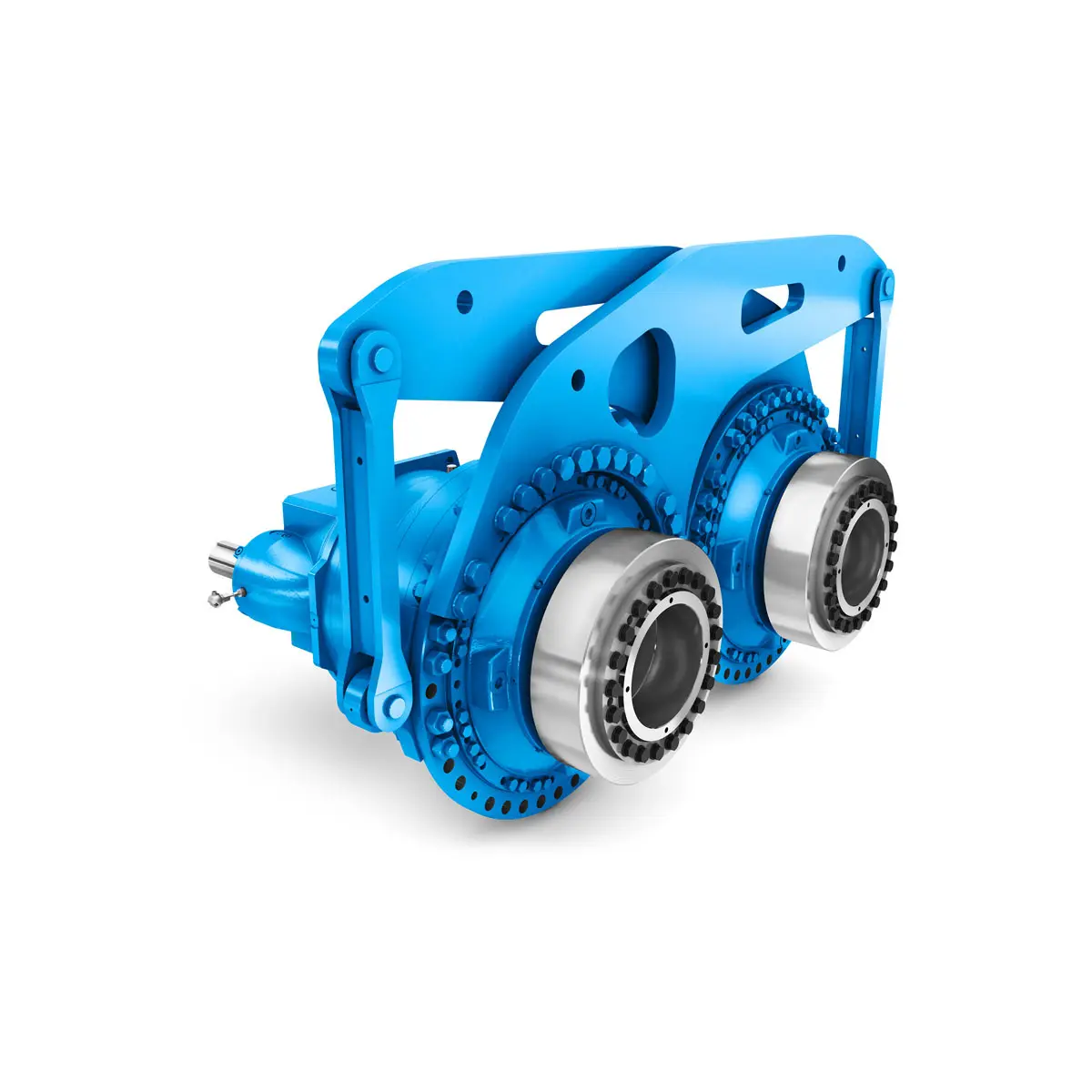 Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.
Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.
-
-
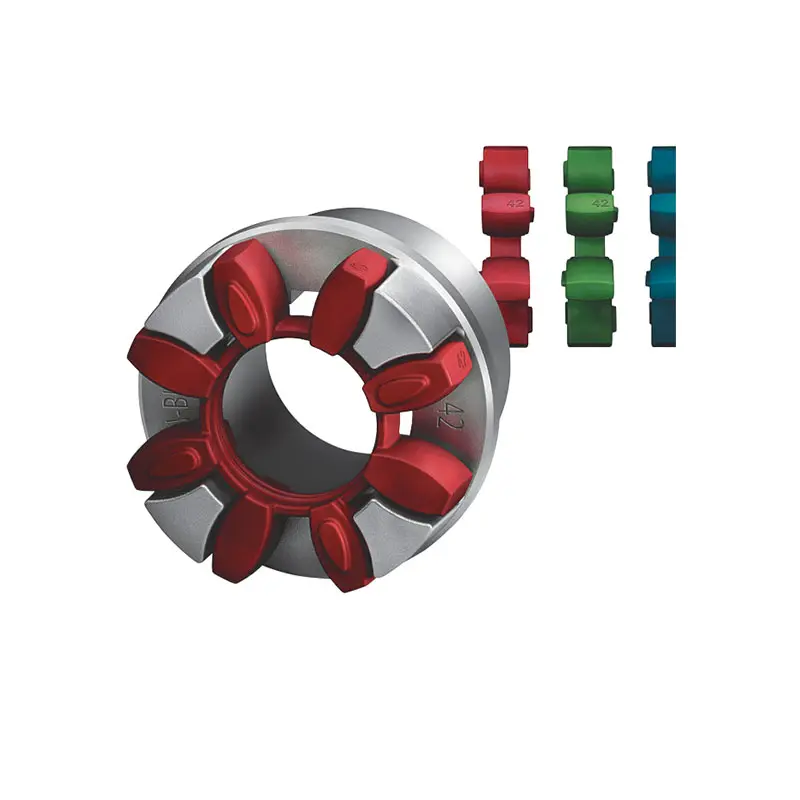 FLENDER Coupling
FLENDER Coupling -
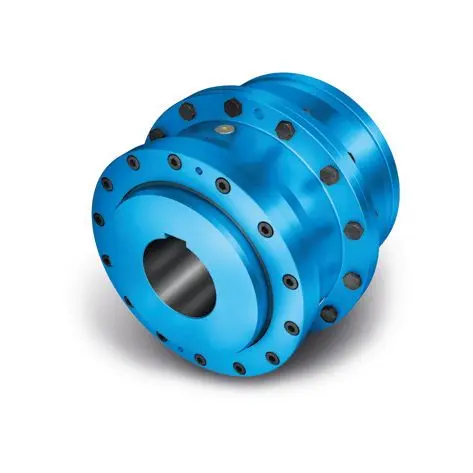 ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling -
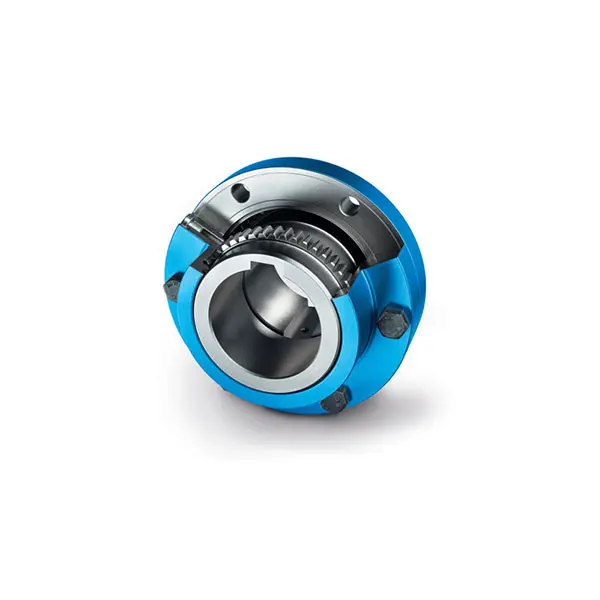 ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling -
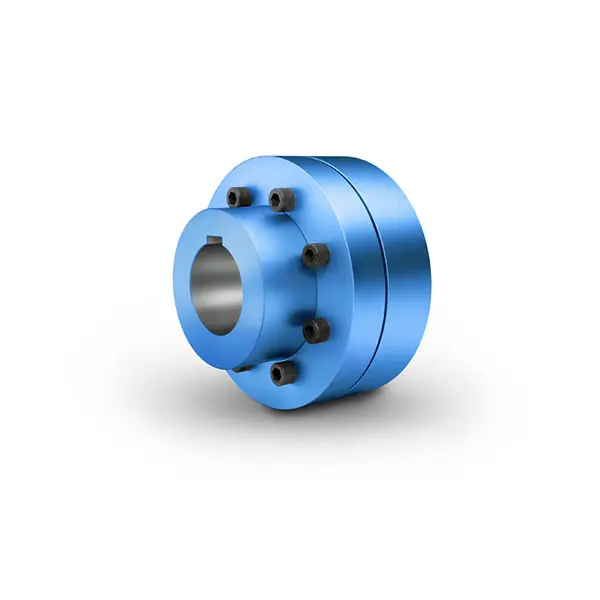 N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling -
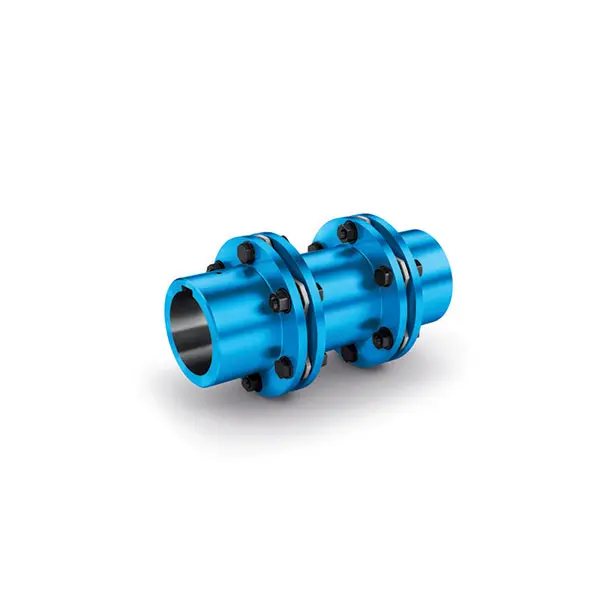 N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling
N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling -
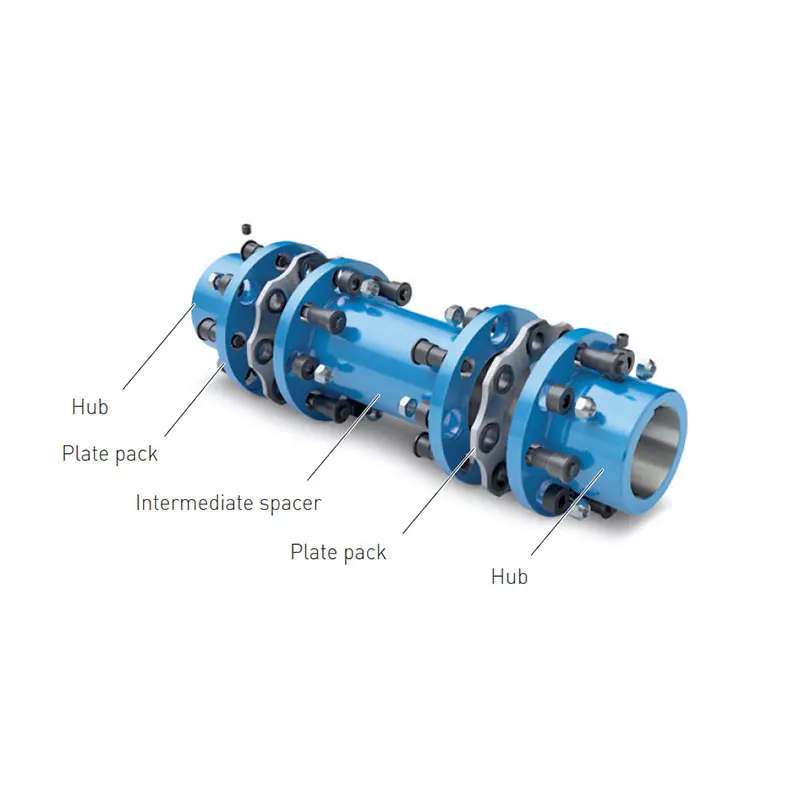 ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts
ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts -
 N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling
N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling -
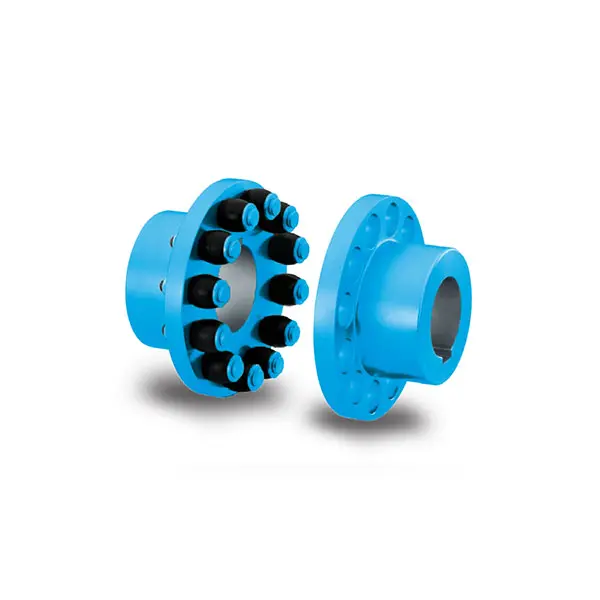 RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling -
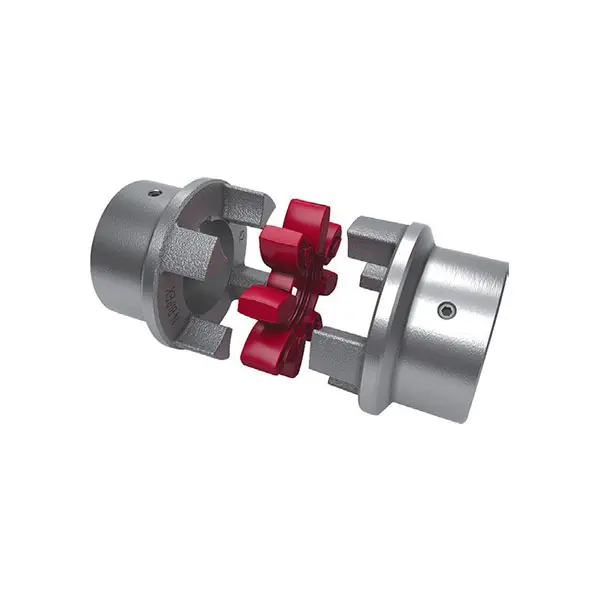 N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling
N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling -
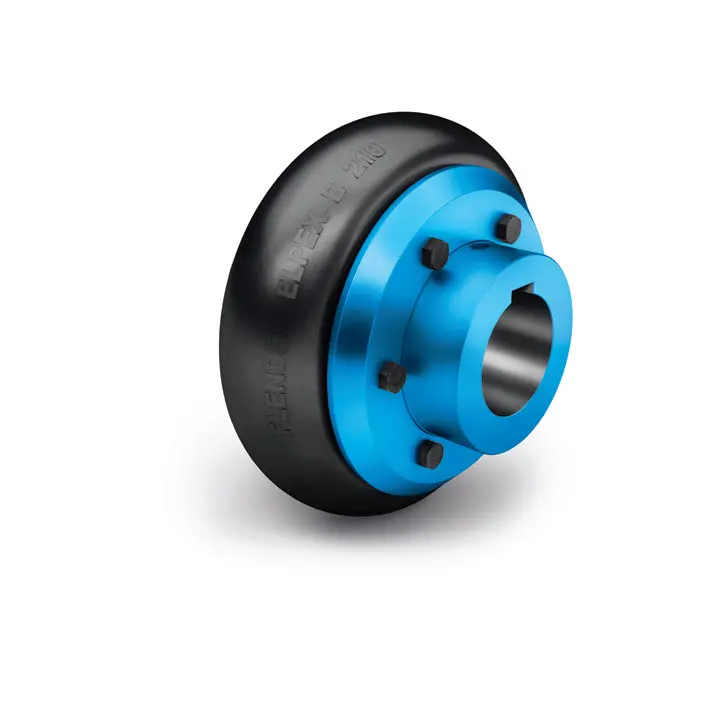 ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling
ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling -
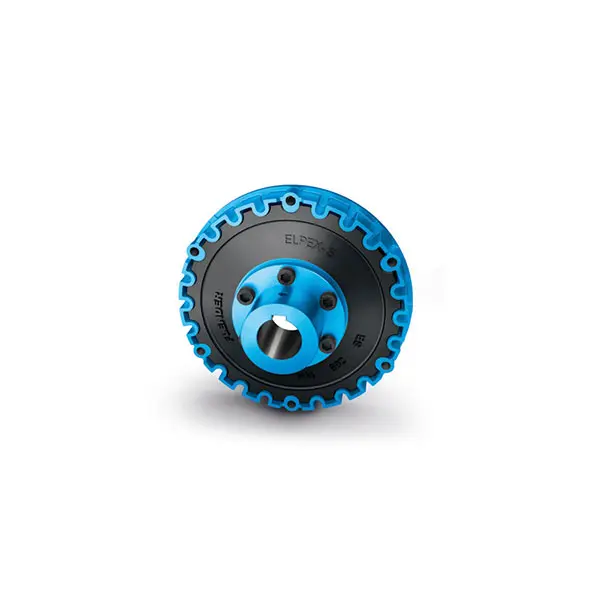 ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance -
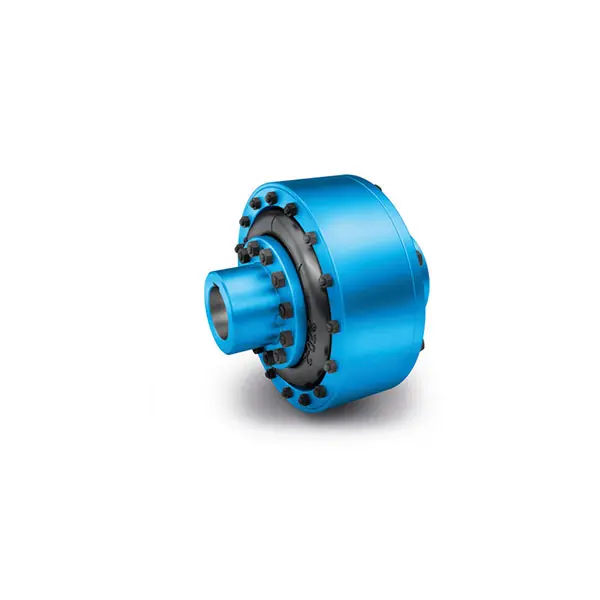 ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance -
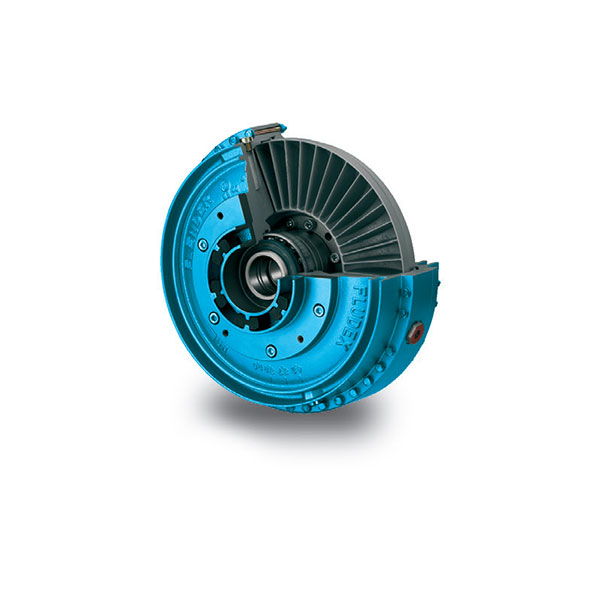 FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance
FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance -
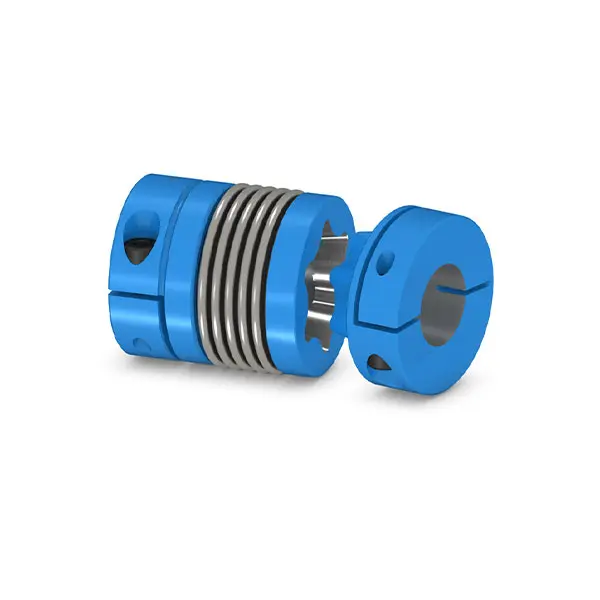 SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance
SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance -
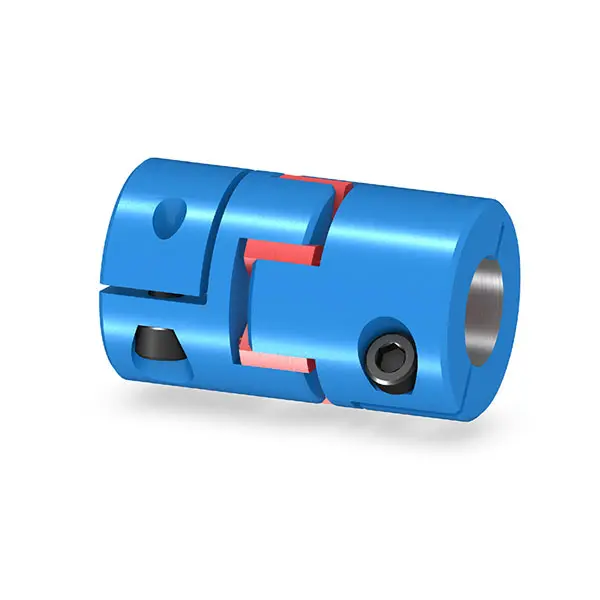 BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance
BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance -
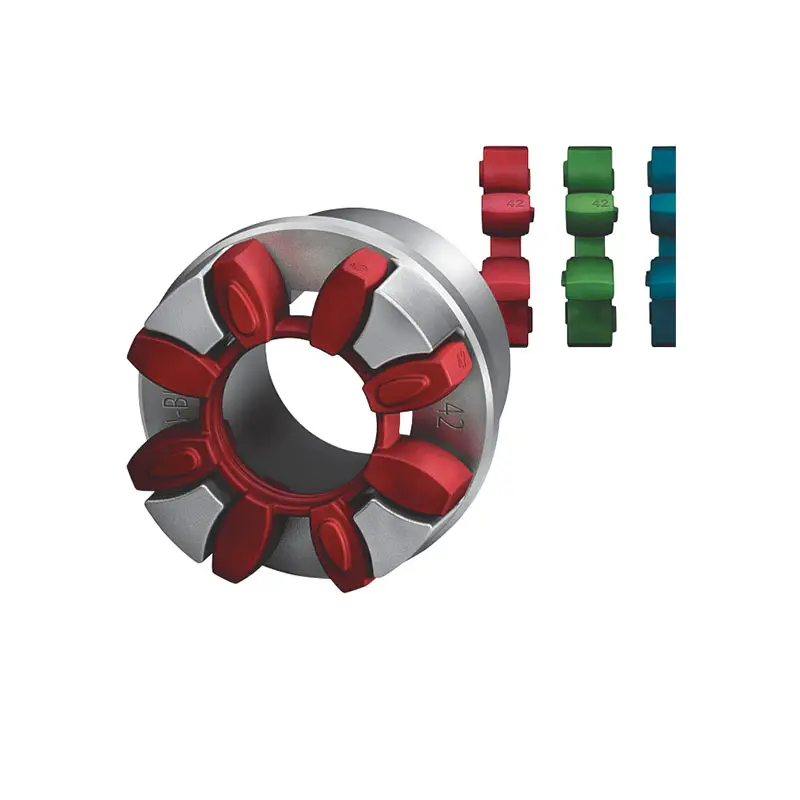 FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance
FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance
-
-
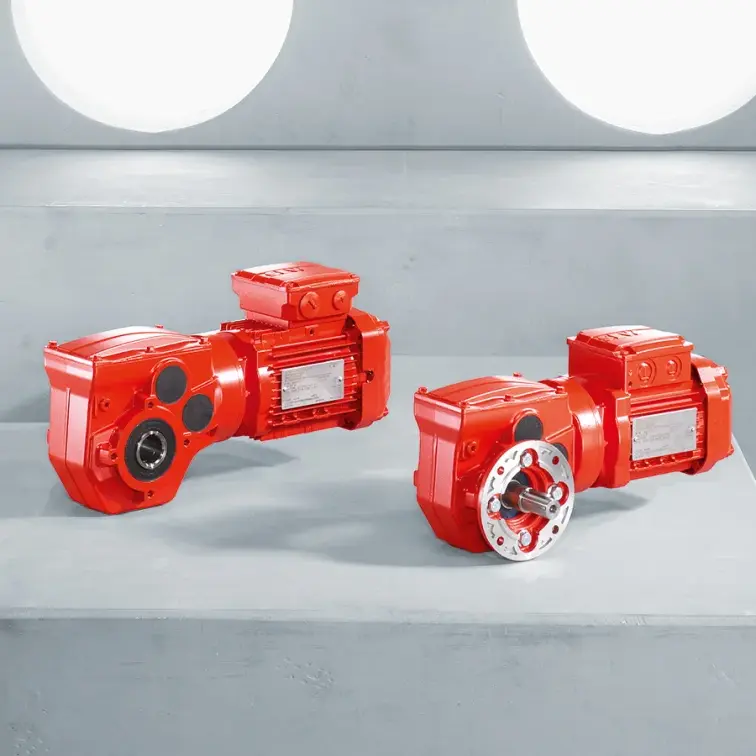 SEW Gearmotor
SEW Gearmotor
-
-
Our Company
-
News
-
Case
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
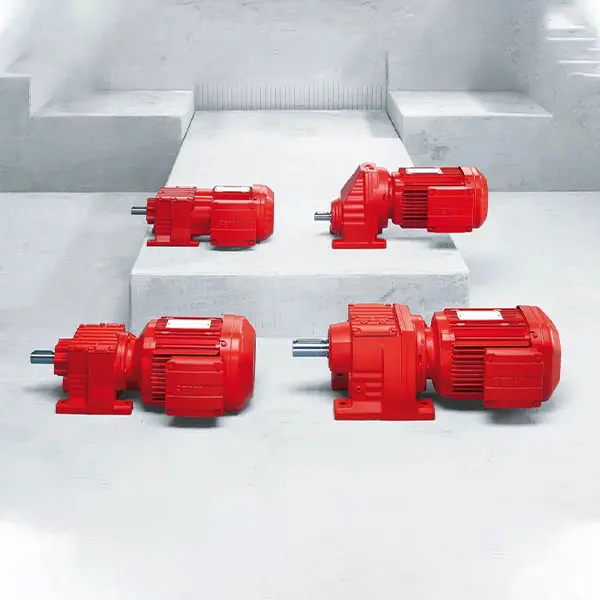 R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage
R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage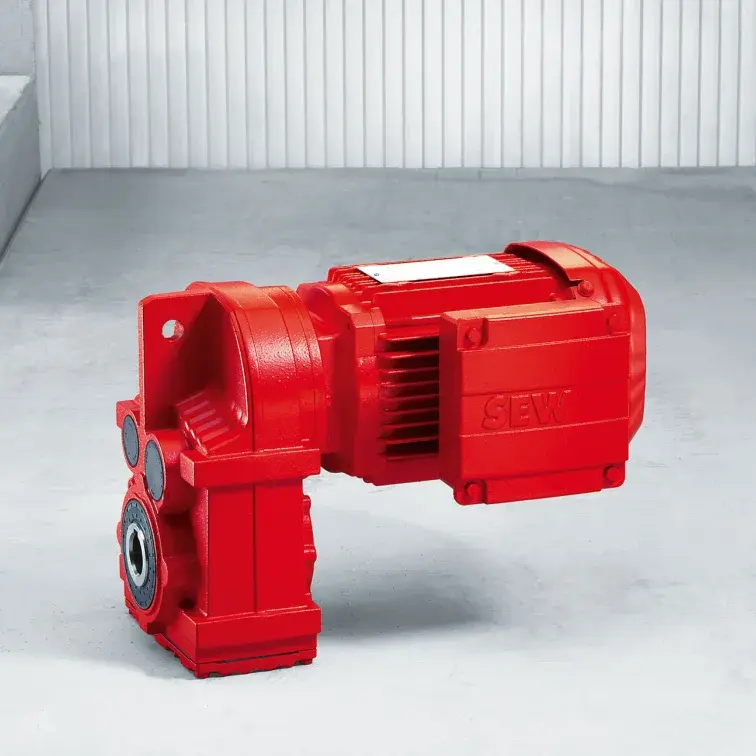 F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage
F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage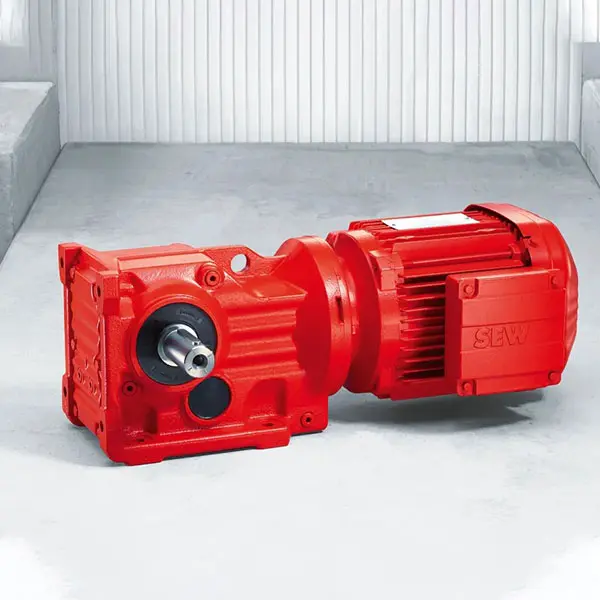 K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage
K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage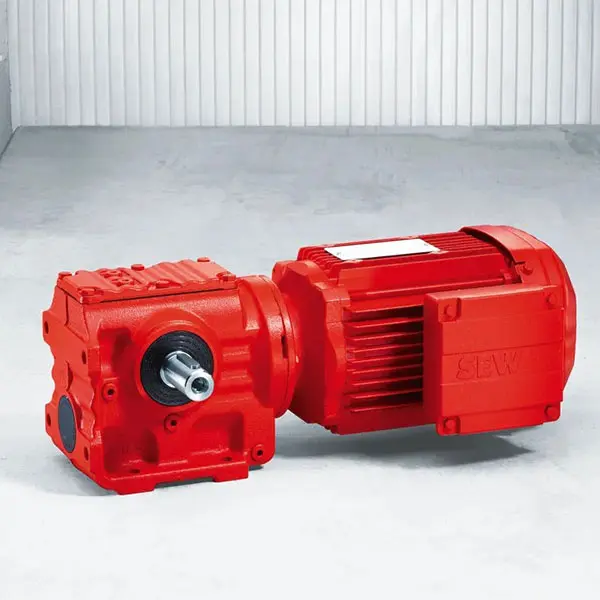 S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage
S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage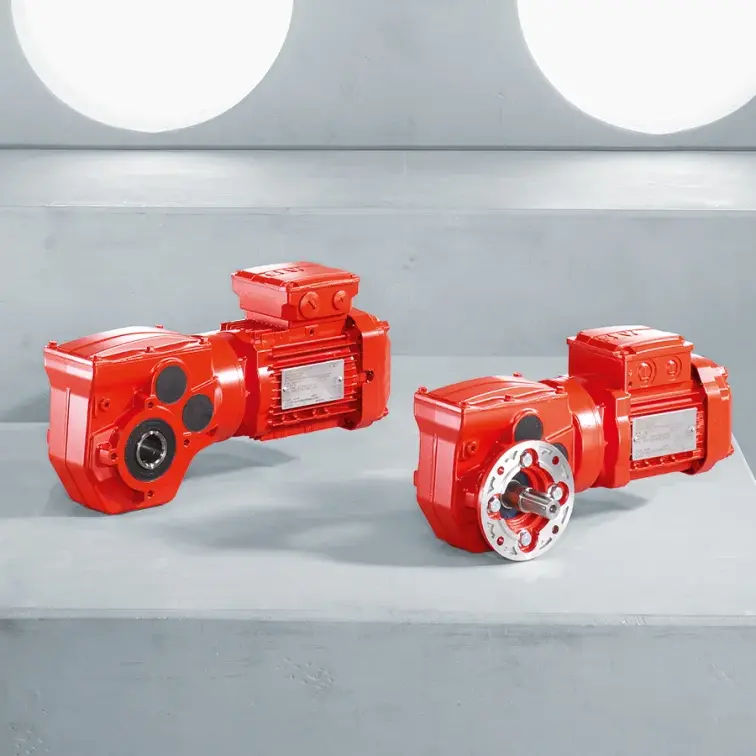 W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor
W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor